2015 Hiroyuki Ok.M. Tanaka
GPS is now a mainstay of each day life, serving to us with figuring out areas, navigation, monitoring, mapping, and timing throughout a broad spectrum of functions. But it does have a few shortcomings, most notably not having the ability to move via buildings, rocks, or water. That’s why Japanese researchers have developed an alternate wireless navigation system that depends on cosmic rays, or muons, as an alternative of radio waves, in line with a new paper printed within the journal iScience. The staff has carried out their first profitable test, and the system might in the future be utilized by search and rescue groups, for instance, to information robots underwater, or assist autonomous automobiles navigate underground.
“Cosmic-ray muons fall equally throughout the Earth and all the time journey on the similar velocity regardless of what matter they traverse, penetrating even kilometers of rock,” stated co-author Hiroyuki Tanaka of Muographix on the University of Tokyo in Japan. “Now, by using muons, we have developed a new kind of GPS, which we have called the muometric positioning system (muPS), which works underground, indoors and underwater.”
As beforehand reported, there may be a lengthy historical past of utilizing muons to picture archaeological constructions, a course of made simpler as a result of cosmic rays present a regular provide of these particles. Muons are additionally used to hunt for illegally transported nuclear supplies at border crossings and to observe energetic volcanoes in hopes of detecting after they would possibly erupt. In 2008, scientists on the University of Texas, Austin, repurposed outdated muon detectors to seek for doable hidden Mayan ruins in Belize. Physicists at Los Alamos National Laboratory have been growing moveable variations of muon imaging methods to unlock the development secrets and techniques of the dome (Il Duomo) atop the Cathedral of St. Mary of the Flower in Florence, Italy, designed by Filippo Brunelleschi within the early fifteenth century.
In 2016, scientists utilizing muon imaging picked up alerts indicating a hidden hall behind the well-known chevron blocks on the north face of the Great Pyramid of Giza in Egypt. The following 12 months, the identical staff detected a mysterious void in one other space of the pyramid, believing it could possibly be a hidden chamber, which was subsequently mapped out utilizing two totally different muon imaging strategies. And simply final month, scientists used muon imaging to find a beforehand hidden chamber on the ruins of the traditional necropolis of Neapolis, some 10 meters (about 33 toes) under modern-day Naples, Italy.
Autonomous robots and automobiles might in the future be commonplace in properties, hospitals, factories, and mining operations, in addition to for search and rescue missions, however there may be not but a common means of navigation and positioning, per Tanaka et al. As famous, GPS cannot penetrate underground or underwater. RFID applied sciences can obtain good accuracy with small batteries, however require a management middle with servers, printers, displays, and so forth. Dead reckoning is stricken by power estimation errors with out an exterior sign to supply correction. Acoustic, laser scanner, and Lidar approaches even have drawbacks. So Tanaka and his colleagues turned to muons when growing their very own various system.
2023 Hiroyuki Ok.M. Tanaka
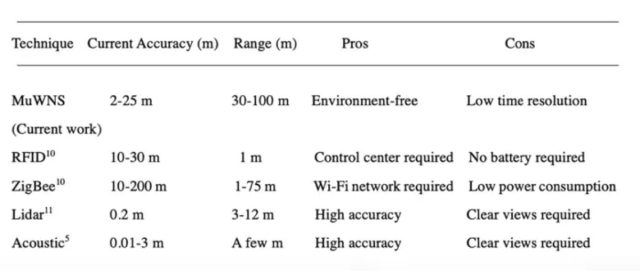
Muon imaging strategies sometimes contain gas-filled chambers. As muons zip via the fuel, they collide with the fuel particles and emit a telltale flash of gentle (scintillation), which is recorded by the detector, permitting scientists to calculate the particle’s power and trajectory. It’s just like X-ray imaging or ground-penetrating radar, besides with naturally occurring high-energy muons reasonably than X-rays or radio waves. That larger power makes it doable to picture thick, dense substance. The denser the imaged object, the extra muons are blocked. The Muographix system depends on 4 muon-detecting reference stations above floor serving as coordinates for the muon-detecting receivers, that are deployed both underground or underwater.
The staff carried out the first trial of a muon-based underwater sensor array in 2021, utilizing it to detect the quickly altering tidal situations in Tokyo Bay. They positioned ten muon detectors throughout the service tunnel of the Tokyo Bay Aqua-Line roadway, which lies some 45 meters (147 toes) under sea degree. They have been in a position to picture the ocean above the tunnel with a spatial decision of 10 meters (practically 33 toes) and a time decision of one meter (3.3 toes), ample to show the system’s potential to sense sturdy storm waves or tsunamis.
The array was put to the test in September of that very same 12 months, when Japan was hit by a hurricane approaching from the south, producing gentle ocean swells and tsunamis. The additional quantity of water barely elevated the scattering of muons, and that variation corresponded nicely to different measurements of the ocean swells. And final 12 months, Tanaka’s staff reported they’d efficiently imaged the vertical profile of a cyclone utilizing muography, displaying the cyclone’s cross sections and revealing variations in density. They found that the nice and cozy core was low-density, in distinction to the high-pressure chilly exterior. In conjunction with current satellite tv for pc monitoring methods, muography might enhance cyclone predictions.
2023 Hiroyuki Ok.M. Tanaka
The staff’s earlier iterations related the receiver to the bottom station with a wire, which restricted motion significantly. This new model—the muometric wireless navigation system, or MuWNS—is, because the identify makes clear, utterly wireless, and makes use of high-precision quartz clocks to synchronize the bottom stations with the receiver. Taken collectively, the reference stations and synchronized clocks make it doable to find out the coordinates of the receiver.
For the test run, the bottom stations have been positioned on the sixth flooring of a constructing and a “navigee” holding the receiver walked across the basement corridors. The ensuing measurements have been used to calculate the navigee’s route and ensure the trail traveled. According to Tanaka, MuWNS carried out with an accuracy of between 2 and 25 meters (6.5 to 82 toes), with a vary of as a lot as 100 meters (about 328 toes). “This is pretty much as good as, if not higher than, single-point GPS positioning aboveground in city areas,” he stated. “But it’s nonetheless removed from a sensible degree. People want one-meter accuracy, and the important thing to that is the time synchronization.”
One resolution can be to include commercially out there chip-scale atomic clocks, that are twice as correct as quartz clocks. But these atomic clocks are too dear in the intervening time, though Tanaka foresees the price lowering sooner or later because the know-how turns into extra broadly included into cellphones. The relaxation of the electronics utilized in MuWNS will probably be miniaturized going ahead to make it a handheld machine.
DOI: iScience, 2023. 10.1016/j.isci.2023.107000 (About DOIs).
The of us at Muographix created this charming fictional animated video to elucidate their muon-based methods.

