Dementia consultants have hailed the most recent landmark within the therapy of Alzheimer’s after Eli Lilly launched trial outcomes that confirmed its new drug considerably slowed reminiscence loss and cognitive decline.
The US prescription drugs group on Monday reported full findings of its section 3 scientific research of donanemab on the Alzheimer’s Association International Conference in Amsterdam, displaying that the antibody therapy slowed progression by about 35 p.c within the early phases of the illness.
The peer-reviewed outcomes observe related section 3 findings launched final November by US biotech Biogen and Japan’s Eisai for lecanemab, one other antibody drug, which acquired full advertising approval from the US Food and Drug Administration this month underneath the model identify Leqembi.
Eli Lilly introduced on Monday that it had submitted donanemab for FDA approval and anticipated a choice earlier than the tip of this yr. Submissions are underway to different international regulators.
Experts on dementia known as Lilly’s donanemab presentation, revealed within the Journal of the American Medical Association, a landmark within the area.
“The past eight months have been a real turning point, as two drugs are shown to slow down the progression of the disease after decades of work with no positive findings,” mentioned Richard Oakley, affiliate director of analysis at UK charity the Alzheimer’s Society.
The donanemab trial concerned 1,736 contributors with a median age of 73 who had delicate to average signs of Alzheimer’s, with half receiving intravenous infusions of the therapy and half a placebo each 4 weeks for 18 months. The drug slowed the progression of the illness most successfully in its earlier phases.
Both lecanemab and donanemab are primarily based on antibodies in opposition to amyloid, one of many poisonous proteins that construct up within the mind as Alzheimer’s proceeds, however they labored at completely different phases of the method, Oakley mentioned.
Lecanemab targets amyloid because it begins to type fibers within the mind whereas donanemab is energetic at a later stage, when the fibers have clumped collectively into bigger accumulations of plaque. The primary adversarial facet impact of each medication was swelling and bleeding of the mind in a small minority of sufferers.
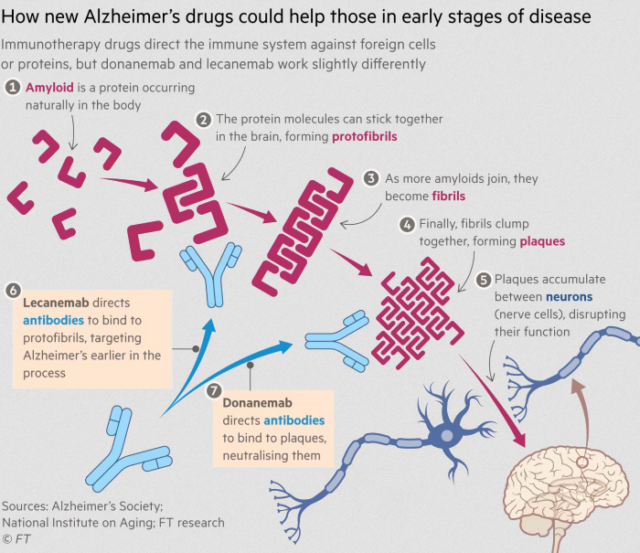
Although the scientific trial designs for the 2 medication make direct comparisons troublesome, there have been tentative indications that donanemab is perhaps simpler than lecanemab when administered to folks within the earliest phases of Alzheimer’s, mentioned Oakley.
It cleared amyloid plaques utterly from the mind in some contributors, who have been then taken off the drug.
Another potential benefit for donanemab, in accordance to Howard Fillit, chief scientist on the US-based Alzheimer’s Drug Discovery Foundation, is that sufferers obtain infusions twice as incessantly for lecanemab—each two weeks.
While Biogen and Eisai have introduced a US listing value of $26,500 a yr for Leqembi, Lilly mentioned it was not but prepared to set the value for its drug.
“With two drugs on the market, we can expect some competition on price,” mentioned Fillit, “but we don’t know yet which factors will play an important role in the marketplace.”
Datamonitor Healthcare forecasts mixed gross sales for the 2 merchandise of $9 billion a yr by 2030 on this planet’s primary markets.
“This is a watershed moment but it is just a start,” mentioned Fillit. “We must continue advancing the drug pipeline to develop the next class centered around the biology of aging to ultimately stop Alzheimer’s in its tracks.”
He added that future therapies can be drug mixtures tailor-made to every particular person via biomarker checks.
© 2023 The Financial Times Ltd. All rights reserved. Please don’t copy and paste FT articles and redistribute by e mail or put up to the net.
