Climate models are a key know-how in predicting the impacts of climate change. By operating simulations of the Earth’s climate, scientists and policymakers can estimate situations like sea degree rise, flooding, and rising temperatures, and make choices about learn how to appropriately reply. But present climate models battle to offer this info shortly or affordably sufficient to be helpful on smaller scales, akin to the scale of a metropolis.
Now, authors of a brand new open-access paper printed in the Journal of Advances in Modeling Earth Systems have discovered a methodology to leverage machine studying to make the most of the advantages of present climate models, whereas decreasing the computational prices wanted to run them.
“It turns the traditional wisdom on its head,” says Sai Ravela, a principal analysis scientist in MIT’s Department of Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary Sciences (EAPS) who wrote the paper with EAPS postdoc Anamitra Saha.
Traditional knowledge
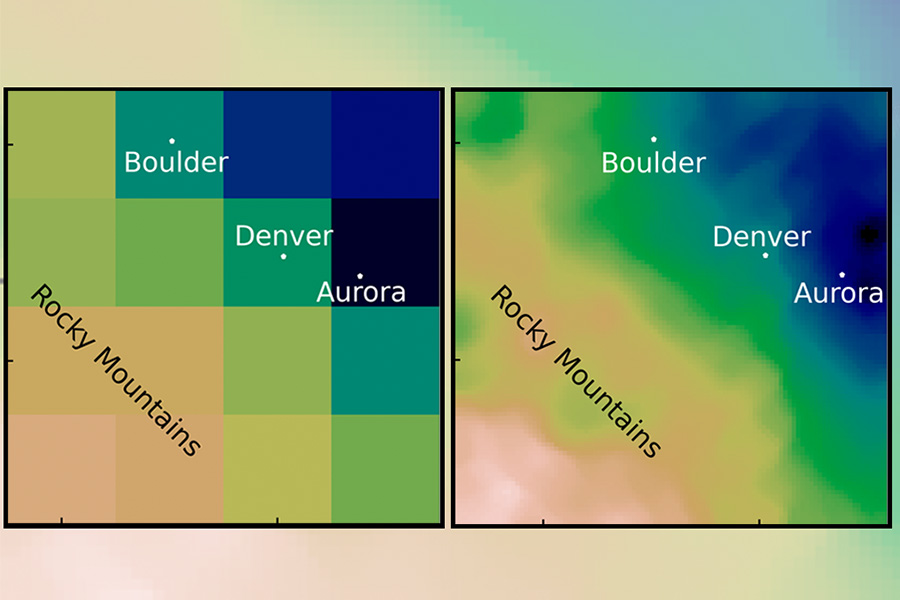
In climate modeling, downscaling is the method of utilizing a world climate mannequin with coarse decision to generate finer particulars over smaller areas. Imagine a digital image: A world mannequin is a big image of the world with a low variety of pixels. To downscale, you zoom in on simply the part of the photograph you wish to have a look at — for instance, Boston. But as a result of the unique image was low decision, the new model is blurry; it doesn’t give sufficient element to be notably helpful.
“If you go from coarse resolution to fine resolution, you have to add information somehow,” explains Saha. Downscaling makes an attempt so as to add that info again in by filling within the lacking pixels. “That addition of information can happen two ways: Either it can come from theory, or it can come from data.”
Conventional downscaling typically entails utilizing models constructed on physics (akin to the method of air rising, cooling, and condensing, or the panorama of the world), and supplementing it with statistical knowledge taken from historic observations. But this methodology is computationally taxing: It takes plenty of time and computing energy to run, whereas additionally being costly.
A little little bit of each
In their new paper, Saha and Ravela have found out a method so as to add the information one other method. They’ve employed a method in machine studying known as adversarial studying. It makes use of two machines: One generates knowledge to enter our photograph. But the different machine judges the pattern by evaluating it to precise knowledge. If it thinks the picture is faux, then the primary machine has to attempt once more till it convinces the second machine. The end-goal of the method is to create super-resolution knowledge.
Using machine studying strategies like adversarial studying is just not a new thought in climate modeling; the place it at the moment struggles is its incapability to deal with massive quantities of fundamental physics, like conservation legal guidelines. The researchers found that simplifying the physics getting in and supplementing it with statistics from the historic knowledge was sufficient to generate the outcomes they wanted.
“If you augment machine learning with some information from the statistics and simplified physics both, then suddenly, it’s magical,” says Ravela. He and Saha began with estimating excessive rainfall quantities by eradicating extra advanced physics equations and specializing in water vapor and land topography. They then generated normal rainfall patterns for mountainous Denver and flat Chicago alike, making use of historic accounts to right the output. “It’s giving us extremes, like the physics does, at a much lower cost. And it’s giving us similar speeds to statistics, but at much higher resolution.”
Another surprising advantage of the outcomes was how little coaching knowledge was wanted. “The fact that that only a little bit of physics and little bit of statistics was enough to improve the performance of the ML [machine learning] model … was actually not obvious from the beginning,” says Saha. It solely takes just a few hours to coach, and may produce ends in minutes, an enchancment over the months different models take to run.
Quantifying danger shortly
Being capable of run the models shortly and sometimes is a key requirement for stakeholders akin to insurance coverage corporations and local policymakers. Ravela provides the instance of Bangladesh: By seeing how excessive climate occasions will influence the nation, choices about what crops ought to be grown or the place populations ought to migrate to may be made contemplating a really broad vary of situations and uncertainties as quickly as doable.
“We can’t wait months or years to be able to quantify this risk,” he says. “You need to look out way into the future and at a large number of uncertainties to be able to say what might be a good decision.”
While the present mannequin solely appears at excessive precipitation, coaching it to look at different important occasions, akin to tropical storms, winds, and temperature, is the following step of the undertaking. With a extra strong mannequin, Ravela is hoping to use it to different locations like Boston and Puerto Rico as a part of a Climate Grand Challenges undertaking.
“We’re very excited both by the methodology that we put together, as well as the potential applications that it could lead to,” he says.