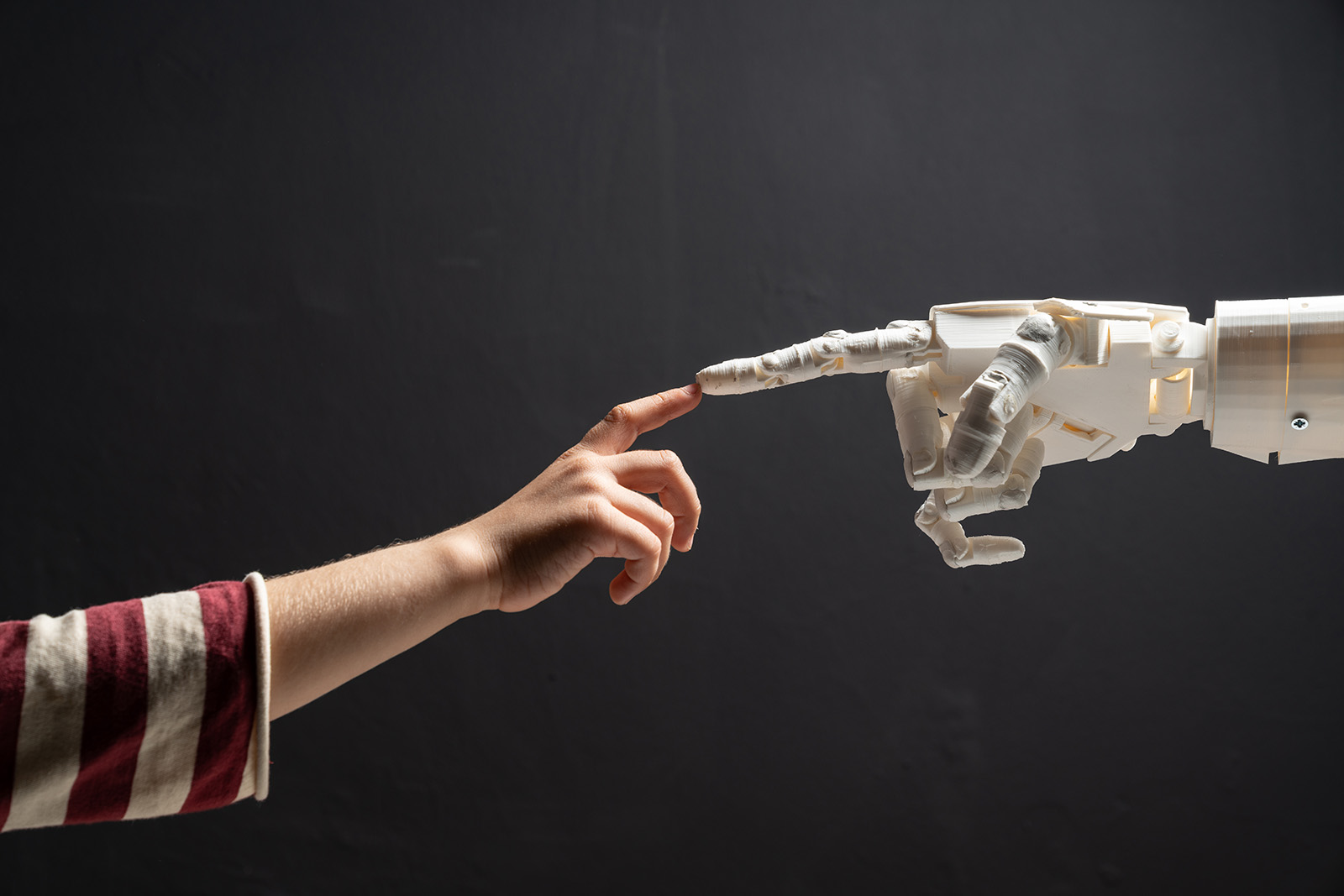
One of essentially the most hanging scenes of Terminator 2, a movie that lately celebrated its thirtieth anniversary, exhibits the robotic hand of the cyborg performed by Arnold Schwarzenegger. Undoubtedly, the fascination generated by the picture responds to the complexity of the motion that replicates the gracefulness of human joints. Until lately, such know-how was the stuff of science fiction. After all, attaining a robotic gadget with the precision, maneuverability, and ranging ranges of accuracy of such a human limb is an actual engineering feat. However, the newest scientific breakthroughs deliver us very shut to that fantasy. And, hopefully, with out the a part of machines changing into aware and taking up the world.
In this text, we’ll clear up some doubts about robotic fingers by addressing these factors:
The new technology of robotic fingers
A group of Korean researchers lately printed a paper within the journal Nature Communications exhibiting probably the most superior robotic hand fashions to date. The key lies not a lot in its energy however in its gentleness. Of course, robots have been utilized in industrial crops because the mid-Twentieth century.
The first of those, referred to as Unimate, was used within the automotive business. This mannequin was outfitted with grippers and will carry heavyweights. But neither it nor its successors may maintain a hen’s egg with out damaging it.
The IDLA (linkage-driven dexterous anthropomorphic) hand is about to change that. The gadget options 4 fingers and a human-style thumb. In addition to their respective joints -twenty in all- these fingers incorporate sensors within the “fingertips.”
The complete measurement is twenty-two centimeters and weighs simply over one kilogram. But what precisely can it do? Here are among the talents of the Korean robotic hand:
- Use precision tweezers
- Use scissors to minimize paper
- Hold an egg or a soda can with out damaging it (and fill a glass when you’re at it).
- Exert a power of up to 34 newtons
The IDLA additionally has the benefit that every one its circuits and programs are built-in into the hand itself, so it may be simply built-in into present robotic arms.
Robotic hand applied sciences
This isn’t the primary time we have now talked about robotic fingers on this web page. Several initiatives showcase the varied approaches to this know-how. Each addresses totally different challenges, from the sense of contact to the power to grasp fragile objects. Here are just a few examples:
- Robotic fingers utilizing static electrical energy. Instead of utilizing stress mechanisms, the Ecole Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL) has investigated the opportunity of utilizing static electrical energy to choose up fragile or brittle objects.
- HASEL, the know-how that mimics human musculature. Human muscle mass contract or broaden in response to electrical stimuli. And that’s the strategy taken by the University of Colorado, the place researchers have used cavities full of a liquid delicate to electrostatic prices. The result’s a hand able to holding a raspberry with out damaging it.
- The sense of contact in robots. Besides the programs for managing grip energy, one of many keys is the sense of contact. At the University of Washington, they’ve developed probably the most superior prototypes on this regard. Their system detects minute vibrations of supplies eight hundred instances per second. If you need to know extra about contact in robots, check out the video beneath:
Applications of robotic fingers
Advances on this area are not restricted to laboratory feats. With a bit of luck, we’ll begin to see these applied sciences in the actual world. Paradoxically, probably the most promising purposes won’t be in robots, however in human prostheses.
Thus, each new tactile programs and stress management applied sciences will allow the event of synthetic fingers.
One of the fashions that has caught our consideration is that of a solar-powered bionic hand. This invention additionally makes use of synthetic intelligence to interpret the indicators from the muscle mass to which it’s hooked up and convert them into actions.
Such robotic fingers are additionally anticipated to have their place in high-precision purposes akin to surgical procedure or the management of equipment in hazardous environments akin to nuclear energy crops.
Sources: TechXplore, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Unimate