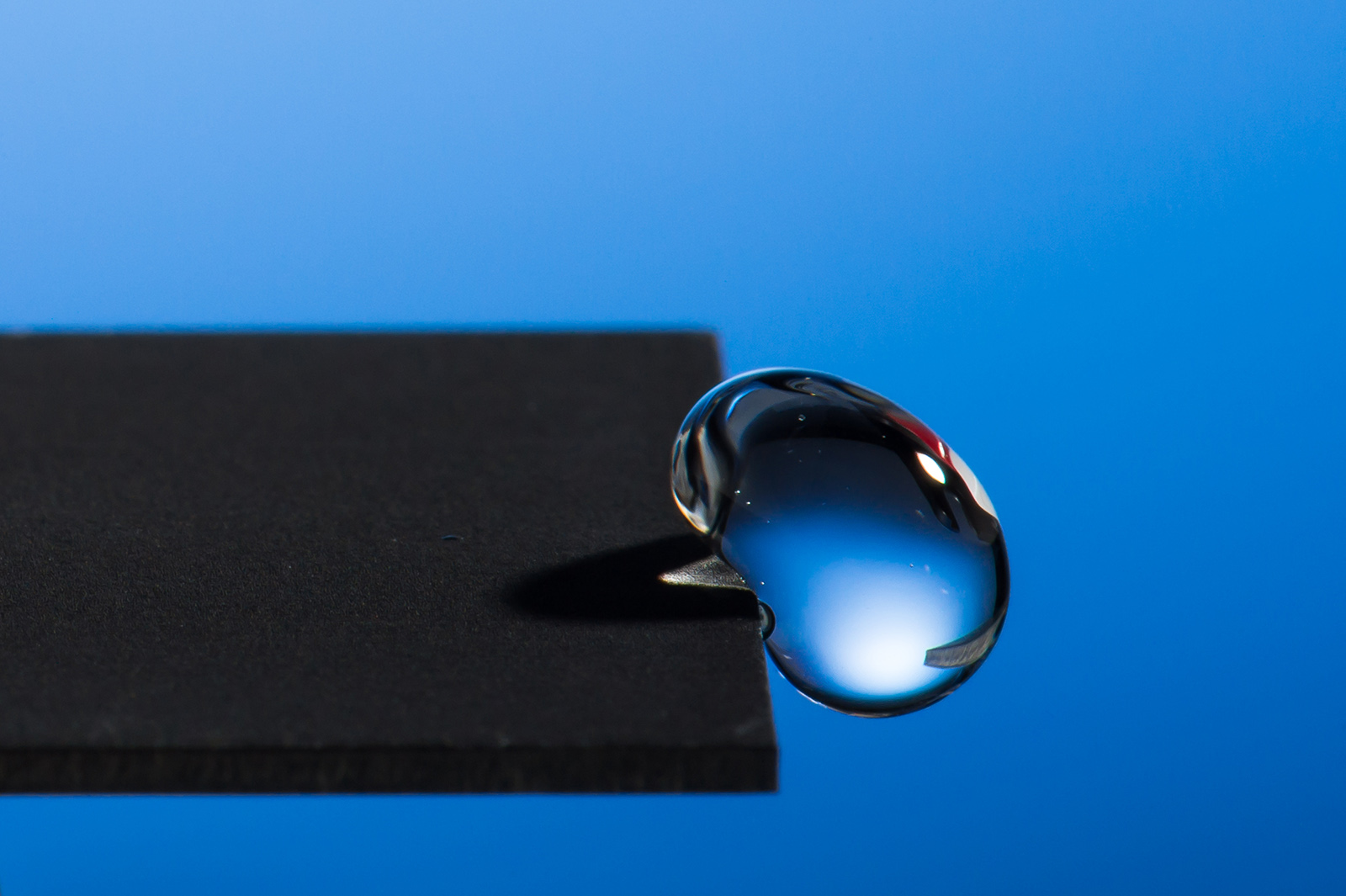
One manner or one other, each residing being on our planet relies on water. That’s why it’s the first factor we search for on different planets in our search of extraterrestrial life. Understandably then, nature has developed a variety of strategies for organisms to seize water from the surroundings—from Californian redwoods that soak up moisture by their leaves and branches all the way in which to the Namibian beetle that harvests water vapor with its exoskeleton. These two examples reveal the flexibility of supplies to seize atmospheric moisture. Redwoods, for example, can cowl one third of their water wants in such a manner, whereas the beetles handle to survive below extraordinarily arid circumstances. As we already mentioned in a earlier article, there are loads of vapor harvesting applied sciences for human consumption. Now, a bunch of scientists from University of Texas has improved the method of water assortment by creating a cloth with a hydrophilic lubricant.
According to their publication within the journal Science Advanced, the important thing lies within the creation of slippery tough surfaces (SRS) with hydrophilic properties and the flexibility to information water droplets in a sure route. These slippery and coarse areas are rather more environment friendly than the prevailing applied sciences, that are primarily based on slippery liquid-infused porous surfaces o (SLIPS). Before going any additional, although, we should always make clear some of these initials. The SLIPS expertise makes use of an progressive porous materials infused with a lubricant fluid. Thus, it achieves a repellant and self-cleaning floor that repels water, but additionally mud specks and different pollution. Inspired by these supplies, in addition to the Namib beetle and pitcher crops, the SRS expertise goes a step additional and fosters the buildup of bigger drops, funneling them into reservoirs by way of lubricated microgrooves.
Therefore, the 2 primary properties of this technological innovation are the flexibility to entice water droplets, as some desert beetles do, and supply an especially slippery floor, because the one supplied by pitcher crops. To that finish, the researchers have leveraged the traits of hydroxy practical teams, that are extraordinarily hydrophilic and are the principle ingredient composing the lubricant. Additionally, the fabric the place the lubricant is utilized sports activities a set of nanotextures that present elevated mobility for the droplets.
Applications of superhydrophilic and superhydrophobic supplies
According to the researchers, the brand new floor would give you the chance to accumulate up to an estimated 120 liters per sq. meter every day. Besides the flexibility to harvest water vapor, the SRS system enjoys a slew of different purposes, whether or not in air con methods, industrial gear, or as a floor to hold ship hulls clear by stopping the buildup of rust and particles.
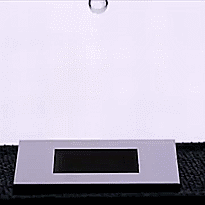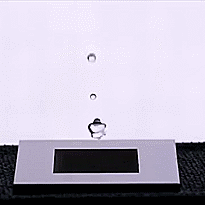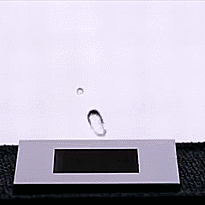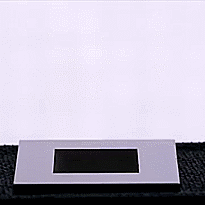
On the opposite hand, there are strategies that make use of carbon nanotubes or laser etching to create superhydrophobic surfaces. These obtain the alternative impact, repelling liquids in an especially environment friendly method and even at occasions inflicting water droplets to bounce on influence. These new supplies can fight rust, ice, and layer over photo voltaic panels to forestall water or impurities from accumulating and lowering their effectivity.
One of probably the most hanging applied sciences on this subject is a cloth developed on the University of British Columbia (UBC), which makes use of {an electrical} present to alternate between superhydrophobic and superhydrophilic states with the flick of a change.
Source: Phys.org

