If you’re a common reader of our website you’ll in all probability be acquainted with the printing of buildings, the colonization tasks in Mars, or the printing of medical prosthesis, with using 3D printing expertise. We have additionally handled using residing organisms comparable to spores to strengthen concrete. Now, the most recent innovation goals to mix the flexibility of 3D printing with the traits of residing supplies, i.e. self-repairing, stimuli-responsive, autonomous and self-replicating. This time, micro organism would be the chosen bioprinting materials.
One of the most recent problems with the Science Advances journal encompasses a paper on the event of a bioink expertise that can be utilized in a 3D printer. The researchers have named it FLINK (Functional Living Ink) and it’s based mostly on bacterial cultures which are later combined with a hydrogel. Professor André Studart, head of the complicated supplies lab of the ETH Zurich college, and his staff have used two several types of micro organism to reveal a few of the many functions that this system may present within the close to future.
The first one, Pseudomonas putida, can break down the poisonous chemical phenol, used within the manufacturing of nylon and different artificial fibers. The second one, Acetobacter xylinum, secretes top quality nanocellulose. This materials can soothe ache and retain moisture, which implies it might be used to develop contoured movies to cowl burns or create pouches for organs to forestall transplant rejection.
The key to the bioprinting course of lies in attaining the suitable viscosity and consistency to allow printing, by being viscous sufficient to be compelled by way of the stress nozzle, and the optimum medium for the event of the bacterial colonies. The hydrogel itself consists of hyaluronic acid, long-chain sugar molecules, and pyrogenic silica. One of some great benefits of the expertise devised by Studart and his staff is its capability to mix up to 4 totally different micro organism, which opens the door for multifunctional inks.
Bioprinted sensors
The ETH researchers predict a large number of functions, with certainly one of them being the event of a microfilm in a position to detect toxins in water, which might be used to cowl the insides of containers storing ingesting water. The analysis of bioinks as high-tech sensors is one other risk explored by MIT labs within the USA. Their design, revealed within the Advanced Materials scientific journal, makes use of micro organism genetically engineered to emit fluorescence within the presence of sure stimuli.
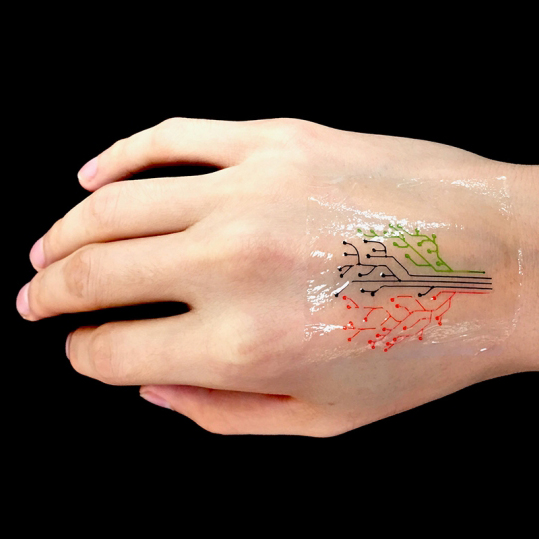

In their bioprinting experiment, additionally based mostly on a bacterial tradition combined with a hydrogel, this time composed of pluronic acid, they printed a tree-shaped tattoo with totally different branches, every certainly one of them with micro organism reacting to particular chemical compounds. Subsequently, they unfold a number of sorts of chemical merchandise on human pores and skin and coated it with a printed layer that had been solidified by exposing it to ultraviolet radiation. Just as they anticipated, the totally different areas of the tree lit up reacting to every chemical product.
These “tattoos” may technically be used to detect biomarkers with regards to swollen tissues or be embedded in wearables like good clothes. In a distant future, probably the most unbelievable functions can be the creation of “living” computer systems with chips made from cells reacting to totally different stimuli.
Source: ETH, MIT