Ultrasound that doesn’t require touching sufferers. An online-based software that reinvents crew scheduling for the Air Force. Cryptographic {hardware} that protects delicate information. And the world’s first sensible reminiscence for quantum networking.
These 4 technologies developed at MIT Lincoln Laboratory, both wholly or with collaborators, acquired 2023 R&D 100 Awards. The ultrasound expertise additionally acquired a second award in a particular class recognizing market-disrupting merchandise. Bestowed by R&D World journal, the awards acknowledge the 100 most important improvements which have transitioned to make use of or been made accessible on the market or license up to now 12 months. The worldwide competitors is judged by a panel of science and expertise specialists and trade professionals.
“Lincoln Laboratory has been very fortunate to receive 86 R&D 100 Awards over the past 14 years. Our rate of unclassified technology transition continues to be very high, and we have a similar high transition rate for our classified programs. The laboratory is truly changing the world through its successful technology development and transition. We congratulate everyone involved,” says Lincoln Laboratory Director Eric Evans.
Medical imaging with noncontact ultrasound
Many persons are aware of the ultrasound course of — a sonographer presses a transducer onto a affected person’s pores and skin and strikes it round, gathering photographs of tissues and organs. Though a well-established expertise, ultrasound suffers from sonographer variability, making it troublesome to precisely examine repeat measurements, and is proscribed by the necessity to make contact with the pores and skin. For these causes, magnetic resonance imaging and computerized tomography, regardless of their excessive prices and lack of portability, are nonetheless the predominant imaging technologies for illness monitoring.
The Noncontact Laser Ultrasound (NCLUS) for Medical Imaging overcomes these limitations. The skin-safe laser system acquires ultrasound photographs with out touching a affected person. It makes use of a pulsed laser that emits optical power, which is transformed to ultrasound waves upon hitting tissue. The returning echoes are detected by a laser Doppler vibrometer and are processed to generate photographs. The system’s laser positioning on the physique could be precisely reproduced, thus eliminating variability throughout repeated scans. This repeatability may allow ultrasound for use to trace illness development, corresponding to modifications in tumor dimension over time.
Its touchless design additionally opens up totally new makes use of for ultrasound: “NCLUS may picture burn or trauma victims, sufferers with open deep-tissue areas immediately throughout surgical procedure, untimely infants requiring intensive medical care, sufferers with neck and backbone accidents, and contagious people from standoff distances,” says Robert Haupt, NCLUS co-inventor.
With NCLUS, medical employees with out sonography coaching may have the ability to carry out ultrasound imaging outdoors of a hospital — in a physician’s workplace, at dwelling, or in a distant battlefield setting. Because of its game-changing potential within the medical imaging trade, NCLUS additionally acquired the R&D 100 Silver Medal within the Special Recognition: Market Disruptor Products class, along with the R&D 100 Award.
Both awards are shared with the Massachusetts General Hospital Center for Ultrasound Research and Translation and Sound & Bright LLC.
An optimizer for aircrew scheduling
The U.S. Air Force has intense scheduling wants. Its fleet of C-17s, the cargo plane that transports troops and provides globally, marked 4 million flight hours final 12 months. Until lately, Air Force airmen, corresponding to pilots and loadmasters, must schedule every flight’s crew manually, on a whiteboard.
Puckboard has modified that. The web-based software offers clever, training-informed scheduling for the primary time since navy flight scheduling started about 80 years in the past, and is returning invaluable time again to airmen to deal with their major duties.
Puckboard’s collaborative instruments present schedulers with task suggestions whereas permitting crew members to volunteer for occasions that work finest for his or her private lives. Beyond offering a digital calendaring operate, Puckboard applies synthetic intelligence methods that take into account metrics corresponding to crew coaching development, flight-hour distribution, overqualification avoidance, and task fragility to suggest optimum schedules. Today, Puckboard hosts 24,000 customers and has scheduled greater than 315,000 occasions throughout 87 squadrons.
“Puckboard’s impact is a direct reflection of the breadth and depth of skill sets and sincere passion that all the contributors have. From the designers, software engineers, and algorithm experts to the active-duty squadrons and aircrew members, all the way up to senior leadership — everyone is committed to increasing the readiness of the U.S. Air Force through the lens of improving the quality of life of our airmen,” says Michael Snyder, a principal investigator on the mission. “Scheduling is a complex topic, made even more difficult under uncertainty, and this effort is a testament to being able to solve any problem with the proper team.”
This R&D 100 Award is shared with MIT, RevaComm, Department of the Air Force – MIT AI Accelerator, Air Force fifteenth Wing, sixtieth Air Mobility Wing, 437th Airlift Wing, Headquarters Air Mobility Command, Air Force Research Laboratory, assistant secretary of the Air Force (Installations, Environment, and Energy), and Raytheon-BBN.
A tool to safe information on uncrewed platforms
For the U.S. navy, using uncrewed programs is rising to attenuate hurt to human operators. Because these programs typically transmit delicate information over the air, their radio parts should be licensed by the National Security Agency (NSA). For years, this certification course of has been an insurmountable hurdle for a lot of small companies and would-be innovators in radio expertise and robotics from which the navy may gain advantage. Now, such builders can use an already-NSA licensed safety answer, developed by Lincoln Laboratory, that’s able to drop in and deploy for all kinds of autos and missions.
The Security/Cyber Module (SCM) End Cryptographic (*100*) (ECU) is a compact system that secures tactical datalinks of uncrewed programs. The module modernizes safety by pulling collectively a number of cybersecurity technologies, most notably a method referred to as Tactical Key Management that establishes secret keys on the fly for safe communication. The module is the primary crypto system designed for a broad swath of uncrewed programs throughout the Joint Communication Architecture for Unmanned Systems (JCAUS), a current U.S. Department of Defense effort to modularize uncrewed system radio hyperlinks and permit reuse of NSA-certified parts by standardizing capabilities and interfaces.
Since its supply, the U.S. Navy has awarded a full-rate manufacturing contract to Tomahawk Robotics to produce SCM ECUs to be used of their explosive ordnance disposal robots. “While developed primarily for Navy ground robotics, the SCM/ECU’s adherence to JCAUS ensures that it is well-suited to airborne and underwater vehicles alike,” says Ben Nahill, a principal investigator on this system.
The award is shared with the Naval Information Warfare Center Pacific.
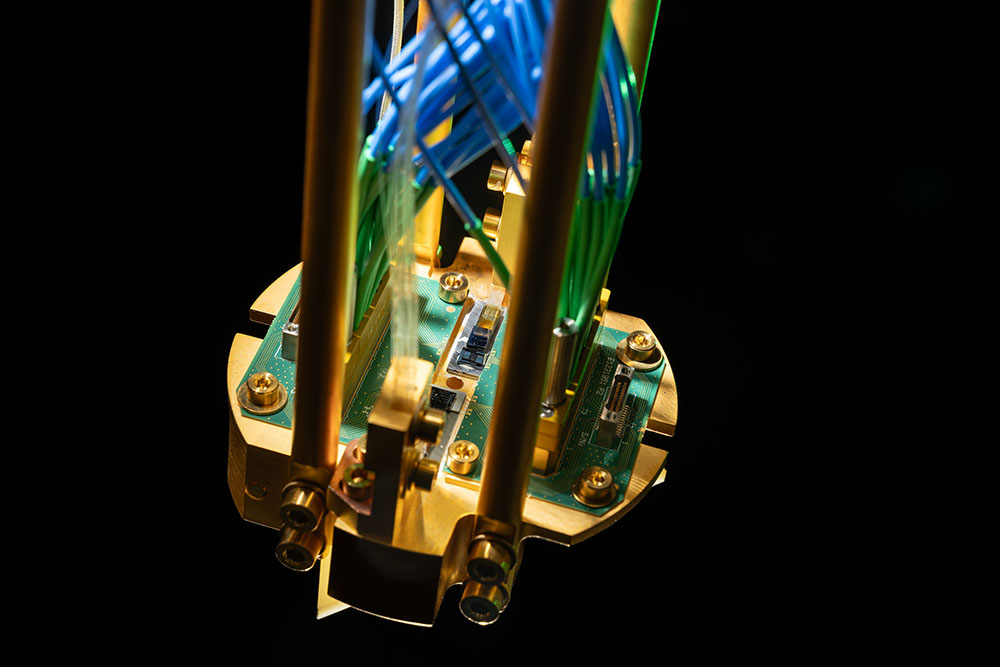
A scalable, photonic reminiscence for quantum networking
In quantum data processing, reminiscence receives and shops the state of a quantum bit (qubit), much like how reminiscence for an bizarre communication system or pc receives and shops data as binary states. Memory makes it doable to reliably ship and obtain data between separate programs, even throughout lossy transmission hyperlinks. Lincoln Laboratory’s quantum reminiscence is the primary to mix, in a single module, the three capabilities required for networking collectively separate quantum programs: a photonic interface, a strategy to appropriate for loss errors, and an structure scalable to tens of reminiscences in a single module. Until now, quantum reminiscence programs have fallen quick on a number of of those capabilities.
“This module eliminates many of the barriers to deploying quantum memories into real-world settings and test beds and to actually using them to develop emerging advanced quantum applications, such as distributed sensing and networked quantum processing,” says Ben Dixon, who leads this work.
A photonic interface permits for qubits to be transferred through particles of sunshine (photons) between the reminiscence and optical-fiber networks. The laboratory’s quantum reminiscence makes use of silicon-vacancy (SiV) diamond color-centers, that are atom-like constructions that may be effectively manipulated with mild, even on the single photon stage. This SiV expertise can even appropriate for signal-loss errors ensuing from inefficient and lossy community hyperlinks. Because it makes use of particular person atomic color-centers, this expertise is appropriate with environment friendly “heralded” protocols, the place a sign confirms the profitable transmission of a photon throughout the community and storage of the related qubit in reminiscence.
The SiV module can also be scalable. The SiV reminiscence cells are built-in to a custom-made photonic built-in circuit, a expertise that allows sending and receiving indicators and could be scaled to tons of of parallel channels. Combining this integration strategy with a singular packaging structure, laboratory researchers built-in eight quantum reminiscences right into a single module. Additional reminiscences could be built-in into this single module, which could be joined with further modules for additional scalability.
In addition to those profitable technologies, five different Lincoln Laboratory technologies have been named R&D 100 award finalists. A gala celebrating the 2023 award winners shall be held on Nov. 16 in San Diego, California.