In March, Tim Cook was among the many first batch of overseas executives to land in Beijing to courtroom high-level officers after the lifting of pandemic-era restrictions, with Apple’s chief lauding how the corporate and China had grown collectively in a “symbiotic relationship.”
Six months on, that relationship is underneath pressure. Apple is dealing with new aggressive pressures in a rustic that’s not solely its largest manufacturing hub but additionally its greatest worldwide market, liable for practically 20 p.c of gross sales in its final quarter.
A share sell-off minimize virtually $200 billion from Apple’s market capitalization this month after information that numerous authorities companies had imposed bans on using Apple merchandise in authorities departments and state-owned enterprises. The Ministry of Foreign Affairs on Wednesday denied any formal prohibition however alluded to iPhone-related “security incidents” and informed smartphone makers to conform with the regulation.
The US was “watching with concern,” a spokesperson for the White House’s National Security Council responded, including that China’s actions seemed to be in line with retaliation in opposition to different US firms as tensions elevated between the 2 superpowers. Apple declined to remark.
Thus far, the corporate has retained an exalted standing in China, avoiding the destiny of different US tech titans, together with Google, Meta, Twitter, and Micron, which have seen merchandise restricted or outright banned.
Cook, chief govt since 2011, has been praised because the “architect” of Apple’s manufacturing shift to China after initially being employed by Steve Jobs in 1998 to run worldwide operations. Under Cook’s management, years of funding, advertising and marketing, and cautious company diplomacy allowed Apple to orchestrate a producing powerhouse whereas producing extra China-based revenue than some other firm, Western or Chinese.
Paul Triolo, an affiliate accomplice at advisory group Albright Stonebridge, mentioned the corporate “invested a lot in its relationships with both the central… and municipal governments, particularly in Zhengzhou,” the place it has partnered with Foxconn and created a whole bunch of 1000’s of jobs. He added that Apple had been “very careful” to abide by native rules, taking down politically delicate apps.
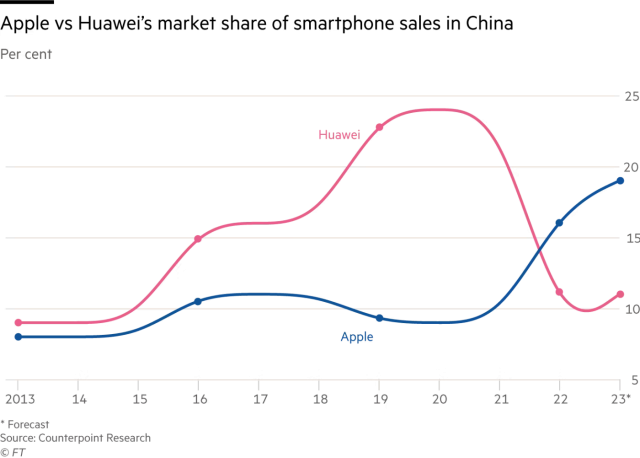
Along with considerations over doable curbs on Apple merchandise, a recent aggressive risk has emerged with the sudden launch of a brand new Huawei smartphone in China on the finish of August. The Mate 60 Pro offered out instantly on a patriotic wave of enthusiasm, as teardown consultants revealed it was working superior Chinese chips inside. US sanctions in opposition to Huawei had beforehand crippled the capabilities of its handsets and enabled Apple to dominate gross sales of high-end smartphones in China.
FT
Apple shares fell additional after the lower than overwhelming launch on Tuesday of the iPhone 15 sequence, however business consultants mentioned the current share falls as a result of occasions in China had been overdone.
Gene Munster, managing accomplice at Deepwater Asset Management, mentioned a “worst case” was that the ban inside the federal government would minimize international iPhone gross sales by 2 p.c and total revenues by 1 p.c in 2024. The Financial Times beforehand reported that restrictions on authorities workers utilizing Apple gadgets already stretched again a number of years.
“Beijing will be very reluctant to take further actions that weaken Apple’s position in China because this would have a very negative impact on the business climate,” mentioned Triolo.
The Apple-China relationship had been a “win-win” for each events, he added. Apple had upgraded Chinese producers’ manufacturing requirements and processes whereas defending its mental property by diversifying its provide chain to make sure nobody provider may replicate its merchandise.
Three former Apple workers with expertise in China advised the corporate was unlikely to be anxious and advised that Beijing seemed to be partaking in some tit-for-tat motion to counter the US’s hardening anti-China insurance policies.
“This shot across the bow wasn’t really to Apple,” one of many folks mentioned. “It was to the US government. This is China flexing.”
China’s lack of any public directive in opposition to Apple additionally contrasts its specific stance when it banned US memory-chip maker Micron from key infrastructure in May, saying it posed “serious network security risks.”
Even so, Cook faces a “delicate balancing act” to diversify extra manufacturing exterior of China whereas sustaining shut ties with Beijing, mentioned one former govt of Foxconn, the Taiwanese firm that assembles the majority of Apple’s iPhones in China.
Apple has 14,000 direct workers in China, however consultants estimate it helps greater than 1.5 million jobs within the nation. Under the pressure of US-China tensions, Apple has begun shifting components of its manufacturing to Vietnam and India.
Against this backdrop, consultants mentioned Beijing can be eager to help homegrown alternate options to Apple corresponding to Huawei—which was briefly the biggest-selling phonemaker on the planet earlier than US sanctions banned it from accessing sure overseas parts, forcing it to discontinue gross sales of its 5G smartphones.
The Shenzhen-based firm’s China gross sales at the moment are supported by its perceived standing as a “national champion” by shoppers, however even its top-of-the-range Mate Pro nonetheless lags the iPhone in technical points.
“Huawei has delivered something that is a generation behind. They’re going to be playing catch-up for a long time,” mentioned Ivan Lam, analyst at Counterpoint Research in Hong Kong, who added that Apple had 80 p.c of the marketplace for telephones priced at greater than $800.
“For Huawei to convert that back to 50:50 will be very challenging, or not even possible.”
Additional reporting by Joe Leahy in Beijing.
© 2023 The Financial Times Ltd. All rights reserved. Not to be redistributed, copied, or modified in any approach.

