It’s no secret that OpenAI’s ChatGPT has some unbelievable capabilities — as an example, the chatbot can write poetry that resembles Shakespearean sonnets or debug code for a pc program. These skills are made attainable by the huge machine-learning mannequin that ChatGPT is constructed upon. Researchers have discovered that when a majority of these models change into massive sufficient, extraordinary capabilities emerge.
But larger models additionally require extra money and time to prepare. The coaching course of includes displaying tons of of billions of examples to a mannequin. Gathering a lot knowledge is an concerned course of in itself. Then come the financial and environmental prices of working many highly effective computer systems for days or perhaps weeks to prepare a mannequin which will have billions of parameters.
“It’s been estimated that training models at the scale of what ChatGPT is hypothesized to run on could take millions of dollars, just for a single training run. Can we improve the efficiency of these training methods, so we can still get good models in less time and for less money? We propose to do this by leveraging smaller language models that have previously been trained,” says Yoon Kim, an assistant professor in MIT’s Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science and a member of the Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL).
Rather than discarding a earlier model of a mannequin, Kim and his collaborators use it because the constructing blocks for a brand new mannequin. Using machine studying, their technique learns to “grow” a bigger mannequin from a smaller mannequin in a method that encodes information the smaller mannequin has already gained. This allows sooner coaching of the bigger mannequin.
Their approach saves about 50 % of the computational price required to prepare a big mannequin, in contrast to strategies that prepare a brand new mannequin from scratch. Plus, the models educated utilizing the MIT technique carried out in addition to, or higher than, models educated with different strategies that additionally use smaller models to allow sooner coaching of bigger models.
Reducing the time it takes to prepare enormous models might assist researchers make developments sooner with much less expense, whereas additionally lowering the carbon emissions generated through the coaching course of. It might additionally allow smaller analysis teams to work with these huge models, probably opening the door to many new advances.
“As we look to democratize these types of technologies, making training faster and less expensive will become more important,” says Kim, senior writer of a paper on this system.
Kim and his graduate scholar Lucas Torroba Hennigen wrote the paper with lead writer Peihao Wang, a graduate scholar on the University of Texas at Austin, in addition to others on the MIT-IBM Watson AI Lab and Columbia University. The analysis might be introduced on the International Conference on Learning Representations.
The larger the higher
Large language models like GPT-3, which is on the core of ChatGPT, are constructed utilizing a neural community structure referred to as a transformer. A neural community, loosely based mostly on the human mind, consists of layers of interconnected nodes, or “neurons.” Each neuron accommodates parameters, that are variables discovered through the coaching course of that the neuron makes use of to course of knowledge.
Transformer architectures are distinctive as a result of, as a majority of these neural community models get larger, they obtain significantly better outcomes.
“This has led to an arms race of companies trying to train larger and larger transformers on larger and larger datasets. More so than other architectures, it seems that transformer networks get much better with scaling. We’re just not exactly sure why this is the case,” Kim says.
These models usually have tons of of hundreds of thousands or billions of learnable parameters. Training all these parameters from scratch is dear, so researchers search to speed up the method.
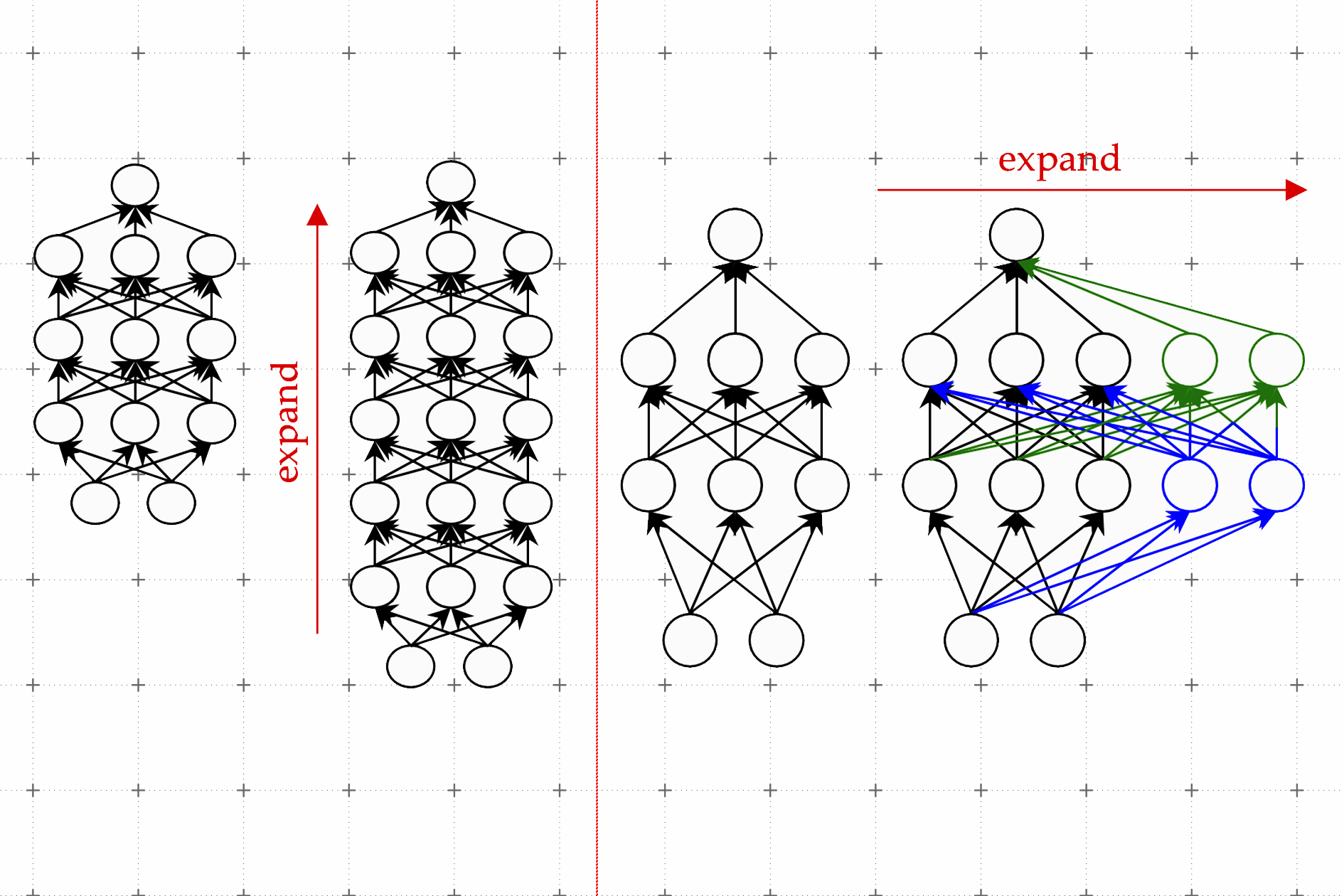
One efficient approach is called mannequin progress. Using the mannequin progress technique, researchers can improve the dimensions of a transformer by copying neurons, and even whole layers of a earlier model of the community, then stacking them on prime. They could make a community wider by including new neurons to a layer or make it deeper by including further layers of neurons.
In distinction to earlier approaches for mannequin progress, parameters related to the brand new neurons within the expanded transformer should not simply copies of the smaller community’s parameters, Kim explains. Rather, they’re discovered combos of the parameters of the smaller mannequin.
Learning to grow
Kim and his collaborators use machine studying to study a linear mapping of the parameters of the smaller mannequin. This linear map is a mathematical operation that transforms a set of enter values, on this case the smaller mannequin’s parameters, to a set of output values, on this case the parameters of the bigger mannequin.
Their technique, which they name a discovered Linear Growth Operator (LiGO), learns to increase the width and depth of bigger community from the parameters of a smaller community in a data-driven method.
But the smaller mannequin may very well be fairly massive — maybe it has 100 million parameters — and researchers would possibly need to make a mannequin with a billion parameters. So the LiGO approach breaks the linear map into smaller items {that a} machine-learning algorithm can deal with.
LiGO additionally expands width and depth concurrently, which makes it extra environment friendly than different strategies. A consumer can tune how broad and deep they need the bigger mannequin to be after they enter the smaller mannequin and its parameters, Kim explains.
When they in contrast their approach to the method of coaching a brand new mannequin from scratch, in addition to to model-growth strategies, it was sooner than all of the baselines. Their technique saves about 50 % of the computational prices required to prepare each imaginative and prescient and language models, whereas usually enhancing efficiency.
The researchers additionally discovered they might use LiGO to speed up transformer coaching even after they didn’t have entry to a smaller, pretrained mannequin.
“I was surprised by how much better all the methods, including ours, did compared to the random initialization, train-from-scratch baselines.” Kim says.
In the longer term, Kim and his collaborators are wanting ahead to making use of LiGO to even bigger models.
The work was funded, partially, by the MIT-IBM Watson AI Lab, Amazon, the IBM Research AI Hardware Center, Center for Computational Innovation at Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, and the U.S. Army Research Office.