Portable flash reminiscence has by no means been extra versatile, and you may be pleasantly shocked by the widespread availability and affordability of high-speed, large-capacity microSD and SD playing cards as of late. Flash storage isn’t just restricted to increasing the reminiscence of your telephone or pill. From drone footage to high-resolution skilled cameras, and steady recording wants of sprint cams and surveillance methods, microSD playing cards have change into the go-to selection for quite a lot of storage wants.
Although microSD playing cards are sometimes favored for his or her compact dimension, full-sized SD playing cards proceed to carry their floor, particularly amongst skilled photographers who demand the utmost reliability and efficiency.
In this information, we clarify all of the completely different card courses and specs, serving to you perceive what is going to work greatest for you. Whether you are an motion digital camera fanatic, a gaming aficionado in search of further storage to your console, or a tech fanatic embarking in your subsequent venture with a Raspberry Pi, this information will present the insights you have to make an knowledgeable selection.
TL;DR: The Highlights
The Basics: Size & Storage
All SD playing cards (quick for Secure Digital), no matter their dimension, use one or two small NAND flash reminiscence chips – much like these present in USB reminiscence sticks and SSDs – and a tiny processor to handle the circulate of information and directions.
There are 3 requirements for the size, and they’re incompatible with one another. In different phrases, a miniSD card reader will not work with microSD playing cards (except you utilize an adapter):
- Standard SD playing cards: 1.26 x 0.94 x 0.083 to 0.055 inches (32 x 24 x 2.1-1.4 mm)
- miniSD playing cards: 0.85 x 0.79 x 0.055 inches (21.5 x 20 x 1.4 mm)
- microSD playing cards: 0.56 x 0.43 x 0.039 inches (15 x 11 x 1 mm)
Standard SD playing cards all include a small locking toggle, that permits/disables the power to put in writing or delete knowledge on the cardboard; nonetheless, mini and microSD playing cards haven’t got this.
There’s additionally an extra 5 classes inside the dimension courses, that point out the connection system and knowledge capability of the cardboard:
- SD or SDSC (Secure Digital Standard Capacity): most storage of two GB
- SDHC (Secure Digital High Capacity): More than 2 to 32 GB of storage
- SDXC (Secure Digital Extended Capacity): More than 32 GB to 2 TB of storage
- SDUC (Secure Digital Ultra Capacity): More than 2 TB to 128 TB of storage
- SDIO (Secure Digital Input Output): Contain extra than simply storage. These playing cards sport an additional machine that gives further capabilities, equivalent to a Bluetooth or GPS receiver.
SDSC is restricted to FAT12, FAT16, and FAT16B. SDHC is almost all the time FAT32 and the XC/HC variations use exFAT. The exFAT file format was particularly designed for NAND flash gadgets and is more likely to stay the usual for a lot of extra years.
SDSC, SDHC, and SDXC playing cards are supported in a variety of gadgets, equivalent to laptops, smartphones, drones, and digital cameras. The want for elevated storage regularly grows, thanks to larger video games, extra complicated apps, and cameras sporting ever larger resolutions – however there’ll all the time be an SD card for everybody’s wants and finances.
SDUC continues to be quite new, so it is going to be a while earlier than we see produces routinely supporting it; 128 TB of storage must be sufficient for almost all of customers for years to come back.
SD Specification Evolution
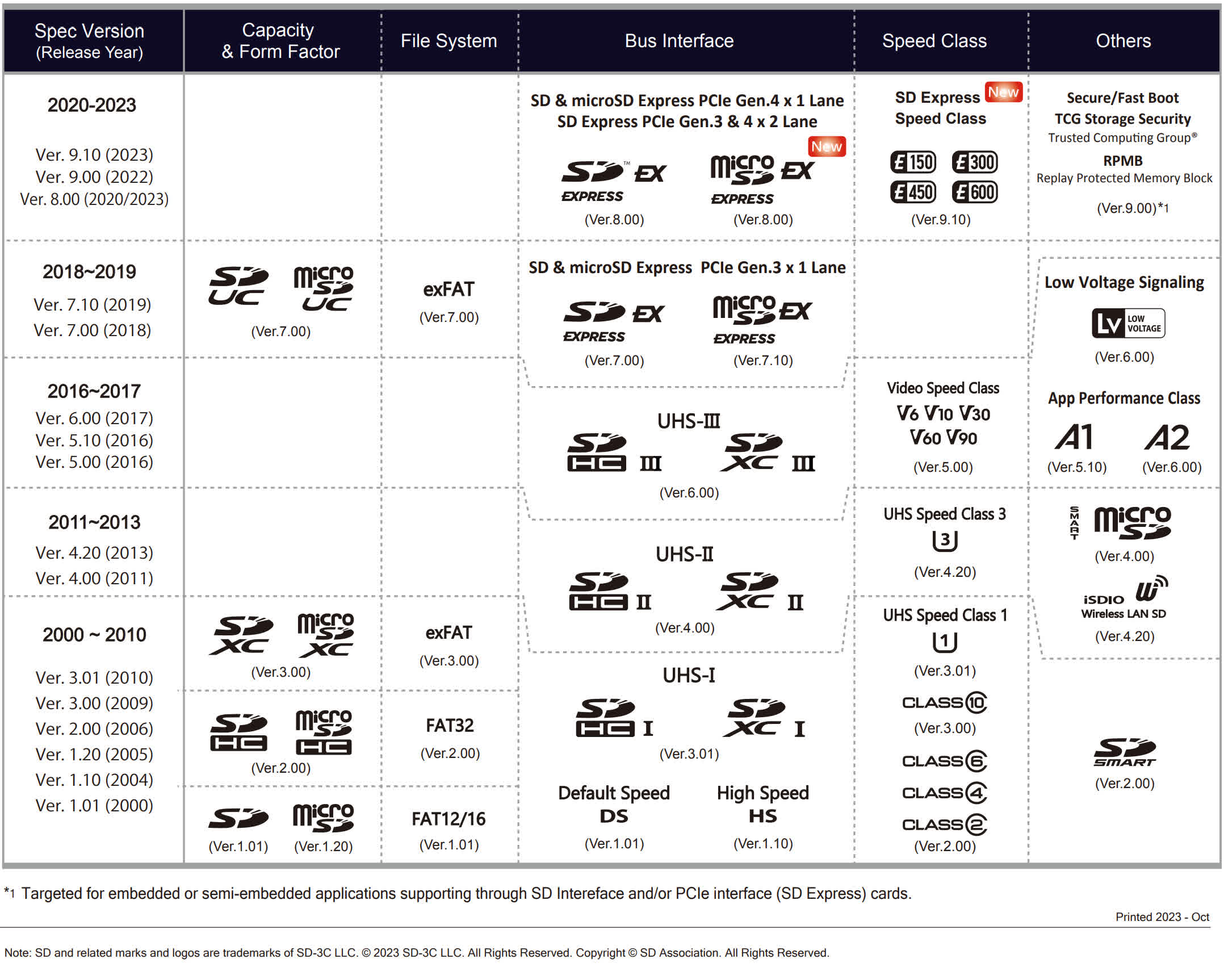
The desk above, from the SD Association, reveals how the Secure Digital expertise has modified over the previous 20 years and highlights simply how rapidly they grew in storage capability. You’ll in all probability have additionally seen that there is much more to SD playing cards than simply capability: time to speak about efficiency.
Performance: Speed Classes
All SD playing cards use the little brass contacts on the finish of the bundle to obtain and ship knowledge. The interface between the cardboard and the studying machine has advanced with every specification revision – in some instances, the up to date system simply runs sooner, however in others, the SD card has further contacts to supply extra channels for the information.
These variations have been labeled in 4 velocity courses, every organized by the height bus throughput – or the measure of the max quantity of bytes per second that may be transferred between the SD card and host machine.
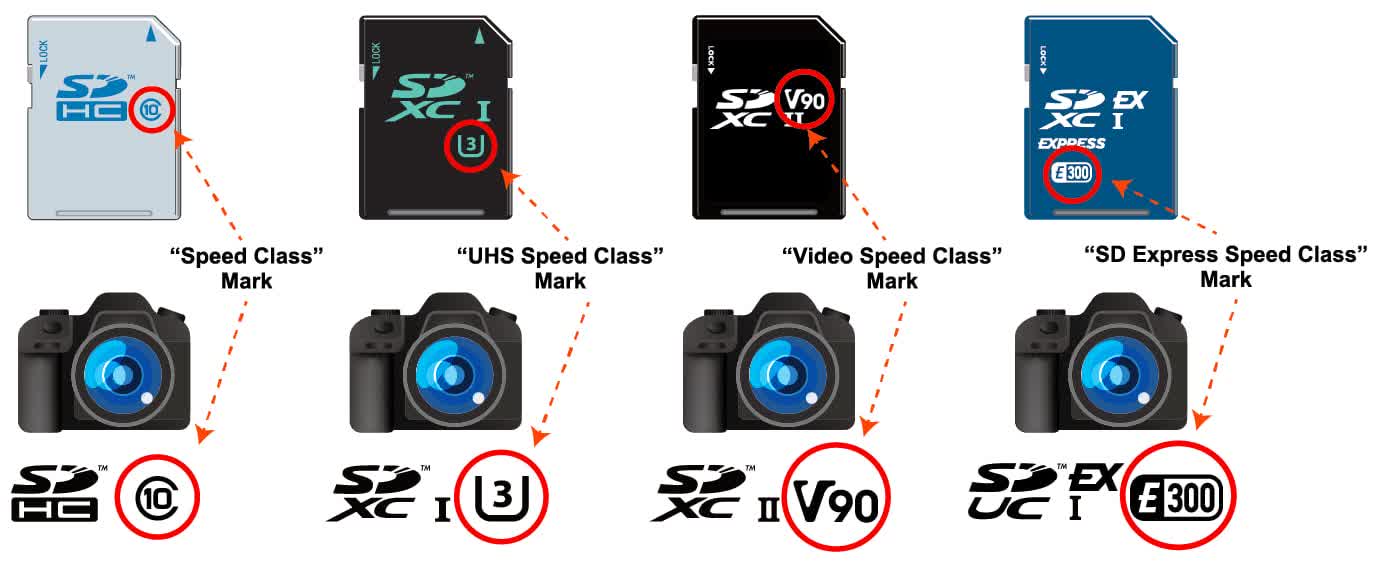

Not all NAND flash chips are the identical, so the velocity courses additionally point out the minimal sequential write charge – the slowest velocity at which knowledge might be put onto the reminiscence chip in a structured, quite than a random, approach.
With so many velocity courses to get your head round, it may be difficult to determine what ranking you actually need. In the desk under, we are able to see how they roughly evaluate.
The SD Association got here up with the velocity classification methods to assist differentiate what playing cards are greatest suited to what functions. The easy Class quantity is probably the most quick indicator to the velocity of an SD card, with Class 2 (2 MB/s) playing cards being towards the underside of the spectrum and are greatest geared in the direction of much less demanding duties, equivalent to recording customary definition video.
At the opposite finish of the dimensions, Class 10 (10 MB/s) playing cards are able to recording or enjoying as much as 4K video, though not at a really excessive body charge.
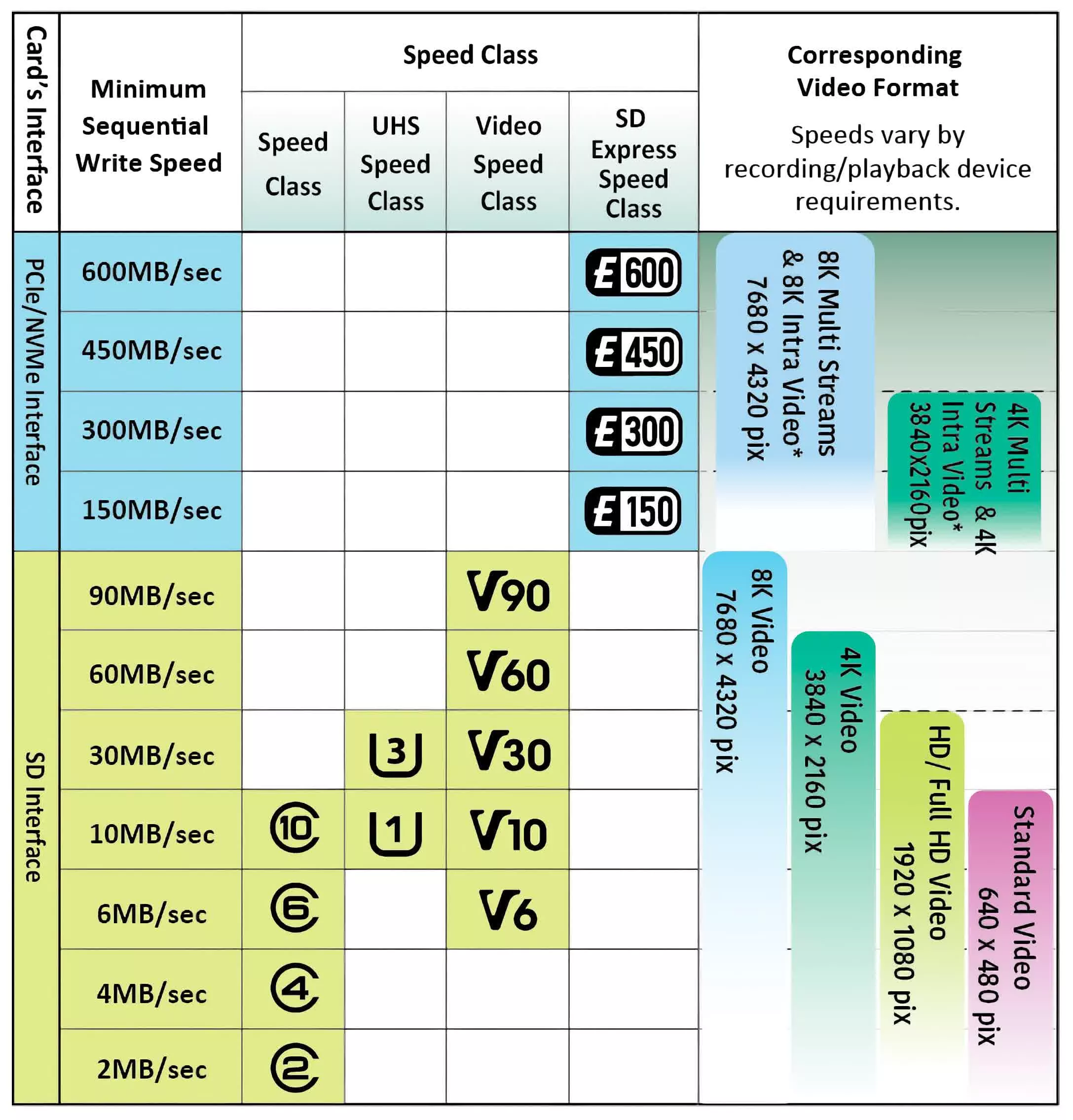
Some SDHC and SDXC playing cards may also help Ultra High Speed (UHS) classification, which presents improved knowledge switch charges. There are 3 variations of this technique and the primary variations to look (UHS-I and UHS-II) provide two velocity modes: U1 and U3. The former is actually the identical as C10, however U3 gives thrice larger throughput at 30 MB/s – ok for 4K movies at a excessive body charges.
UHS-I playing cards have only one set of contacts for sending and obtain data, so when operating on the larger velocity, the bus will run in what is known as Half Duplex mode: the SD card will solely be capable of obtain or ship knowledge, at anybody time. The later variations of UHS sport further contacts, which allows Full Duplex (ship and obtain collectively), each to happen on the similar time; nonetheless, in UHS-II this leads to the bus being compelled to run on the slower velocity. UHS-III and SD Express haven’t got this downside, and all the time run Full Duplex.

With SD Specification 5.0, the affiliation supplied one other ranking system: Video Speed. This classification is healthier at conveying its data, with Video Class 10 (V10), for instance, making use of to playing cards which have a minimal sequential write velocity of 10 MB/s, by to Video Class 90 (V90 = 90 MB/s). At that velocity, the playback and recording of 8K video at 60 to 120 fps turns into possible.
Later on, the SD Association introduced the SD Express specification – this model makes use of as much as 2 PCI Express lanes to supply an enormous enhance in throughput.
SD Card Bus Speeds
| Bus system | Peak throughput (MB/s) | PCI Express kind | SD card supported | |
| Default velocity (DS) | 12.5 | Not used | All | |
| High Speed (HS) | 25 | Not used | All | |
| Ultra High Speed I (UHS-I) | 50 | 104 | Not used | SDHC, SDXC, SDUC |
| Ultra High Speed II (UHS-II) | 156 | 312 | Not used | SDHC, SDXC, SDUC |
| Ultra High Speed III (UHS-III) | 312 | 624 | Not used | SDHC, SDXC, SDUC |
| SD Express | 985 | PCIe 3 (x1 lane) | SDHC, SDXC, SDUC | |
| SD Express | 1970 | PCIe 4.0 (x1 lane) PCIe 3 (x2 lanes) |
SDHC, SDXC, SDUC | |
| SD Express | 3940 | PCIe 4.0 (x2 lanes) | SDHC, SDXC, SDUC | |
SD playing cards using UHS-III or SD Express sooner specs aren’t extensively out there, regardless of the applied sciences being out there for a number of years. But it is because the efficiency is just unlocked if the machine utilizing the cardboard absolutely helps it, and that help stays largely absent.
| SD Express Speed Class | Minimum learn/write efficiency (MB/s) |
| SD Express E150 | 150 |
| SD Express E300 | 300 |
| SD Express E450 | 450 |
| SD Express E600 | 600 |
Briefly proven within the very first desk is one more class ranking. The use of SD playing cards in smartphones and tablets, the place the extra NAND flash can be utilized as working storage, requires extra than simply good throughput. The capacity to deal with plenty of random knowledge directions (measured in IOPs, enter/output operations per second) is vital to making sure constant system efficiency, and in 2015 the SD Association created two additional requirements: Application Class A1 and A2.
Cards rated A1 are succesful good for a random learn efficiency of 1500 IOPS and random writes of 500 IOPS, whereas A2 considerably will increase that, though this does require very particular {hardware} help. Additionally, the A1/A2 ranking additionally signifies that the playing cards presents a sustained sequential write velocity equal to that of V10.
| Class | Min. Seq. Writes | Min. Random Read | Min. Random Write | Ideal Workload |
| A1 | 10 MB/s | 1500 IOPS | 500 IOPS | Editing and updating utility knowledge, not simply storage |
| A2 | 10 MB/s | 4000 IOPS | 2000 IOPS | Specialized makes use of of the above |

All of this makes the ranking system considerably of a minefield to navigate, however usually talking, it may be damaged down into 3 easy classes: normal use/worth for cash, very best efficiency, and most storage capability.
For instance, the common smartphone consumer will want one thing from the primary class, whereas a high-end digital camera or video recorder, utilized by knowledgeable photographer, will need to take into account one thing from the opposite two extra specialised classes.
What to Buy
Although this information ought to have geared up you with the knowledge you have to choose your personal SD or microSD card, we went forward and selected fashions for the three classes that stood out as providing the very best mixture of specification and value. We’re conserving this information up-to-date all year long the place probably the most infamous variations are within the capability and worth now you can get, primarily now you should purchase a lot bigger reminiscence playing cards for comparatively much less.
Best Value microSD Cards
Best Value SD Card
Samsung’s driving pressure within the flash drive market shouldn’t be restricted to high-speed SSDs and there is a good probability that the corporate’s reminiscence chips are in your telephone, too. Thus, it should not come as a shock to see a Samsung-branded microSD playing cards listed right here.

For solely $23, the 256GB Samsung Pro Plus (UHS-1, U3) presents as much as 180 MB/s reads and 130 MB/s writes, and it ships with an SD card adapter.
You also can select a card with much less capability. The similar Samsung microSD card with 128GB is right down to $13. There are loads of alternate options, however you have to be conscious that many are U1 playing cards; they promote the identical learn speeds because the Samsung playing cards, however they’ve a lot slower writes of solely 20-30 MB/s.
Best High Performance microSD Cards
- Smartphone/Tablet use: SanDisk Extreme 256GB UHS-I U3/V30 A2 – $30 on Amazon
- Video recording: Lexar Professional 1066x 256GB UHS-I U3/V30 A2 – $23 on Amazon
- Runner up: ProGrade Digital 256GB UHS-II U3/V60 – $109 on Amazon
Best High Performance SD Cards
For a large majority of customers, the very best worth playing cards will likely be quick sufficient and will provide loads of storage. However, for extra specialised use, be sure you are shopping for a prime performing card that is proper for the duty, and that your machine can take full benefit of the cardboard’s ranking.
If you need quick storage for a smartphone or pill, you have to be extra involved about quick random entry and studying small recordsdata concurrently. The SanDisk Extreme 256 GB is rated for sooner A2 utility efficiency (4000 learn and 2000 write IOPS) and lists 200 MB/s sequential reads with 140 MB/s write speeds.
For film recording on drones and video gear, you need a card with the very best ranking (UHS-II V60). The ProGrade Digital has been rated for 4K video recording and is comparatively inexpensive at $109 for 256 GB.
UHS-II rated microSD playing cards are usually extra scarce, however might be present in numerous manufacturers for those who search for them (the cardboard reader should be UHS-II rated to make the most of the sooner reminiscence).
If you need the very best efficiency on full dimension SD, prime performing SD playing cards equivalent to Lexar Pro 2000x and the Sony Tough-G can attain 300 MB/s reads and higher sustained writes within the bigger kind issue.
Best High Capacity microSD Card
- More storage: Lexar Play 1 TB UHS-I U3/V30 A2 – $73 on Amazon
- Good Alternative: Lexar Pro 1066x 256GB UHS-I U3/V30 A2 – $45 on Amazon
Best High Capacity SD Card
- More storage: SanDisk Extreme Pro 1TB SDXC UHS-I U3/V30 – $140 on Amazon
- Faster Alternative: Lexar Silver Pro 1TB SDXC UHS-II U3/V60 – $269 on Amazon

If you merely want the max quantity of storage you may get, 1TB playing cards are extra inexpensive than they had been earlier than. You will not discover something greater for the worth than Lexar’s Play 1 TB (UHS-1, U3/V30) on the microSD facet. It may appear costly at $73, however if you’re routinely capturing 4K video, then you definitely’ll welcome the additional capability.
When it involves the SD format and needing the very best capability and storage, two prime choices emerge: the SanDisk 1TB Extreme (UHS-1, U3/V30, A2) and the sooner Lexar Silver Pro (UHS-II, U3/V60). Both provide a superb stability between efficiency and capability, making them ideally suited decisions if you would like the capability and are prepared to pay a premium for it.

