Getty Images
For three days, system directors have been troubleshooting errors which have prevented Windows customers from operating purposes corresponding to QuickBooks and Avatax. We now know the trigger: an unannounced transfer or glitch by Microsoft that removed a once-widely used digital certificate in Windows.
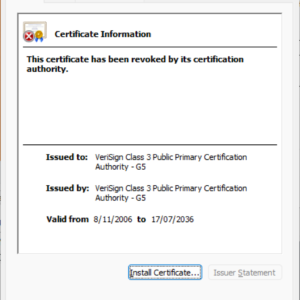
The removed credential is named a root certificate, which means it anchors the belief of tons of or 1000’s of intermediate and particular person certificates downstream. The root certificate—with the serial quantity 18dad19e267de8bb4a2158cdcc6b3b4a and the SHA1 fingerprint 4EB6D578499B1CCF5F581EAD56BE3D9B6744A5E5—was now not trusted in Windows. Because that root was tied to certificates that certify their authenticity and belief, folks attempting to make use of or set up the app acquired the error.
Just minutes earlier than this submit was scheduled to go stay, researchers realized that the certificate had been restored in Windows. It’s unclear how or why that occurred. The certificate instantly under this paragraph reveals the certificate’s standing on Thursday. The one under that reveals the standing as of Friday.
That time Symantec certs have been banished from the Internet
Microsoft has but to reply to a request to elucidate the errors. It could also be {that a} glitch prompted Windows to take away the basis certificate. It’s additionally doable the elimination was intentional, provided that it’s one in every of a number of that confronted an industry-wide blockade following the invention in 2015 that its father or mother issuer on the time, Symantec, had improperly issued certificates for google.com, www.google.com, and one different area. (Symantec bought its certificate authority (CA) companies to DigiCert in 2017.)
After Google researchers asserted a couple of weeks later that the variety of mis-issued certificates was a lot increased, Symantec revised the quantity to 164 certificates for 76 domains and a couple of,458 certificates for domains that had by no means been registered. In gentle of the brand new data, Google gave Symantec an ultimatim: give a radical accounting of its ailing certificate authority course of or threat having the world’s hottest browser—Chrome—subject scary warnings about Symantec certificates each time finish customers visited HTTPS-protected web sites that used them.
Some 17 months later, Google made good on the risk after its investigation concluded that for years, Symantec-owned CAs had improperly issued greater than 30,000 certificates. The firm started preparations to step by step nullify Chrome’s belief in all certificates issued by these CAs, which have been bought below manufacturers together with Verisign, Thawte, and GeoTrust. Effective instantly at the moment, Chrome stopped recognizing any prolonged validation standing of such certificates, and as time went on, the browser revoked increasingly of its belief.
Mis-issued certificates signify a essential risk to nearly the complete Internet inhabitants; they make it doable for the holders to cryptographically impersonate the affected websites and monitor or tamper with communications despatched between guests and the professional servers. In explicit, certificates for non-existent domains or domains belonging to events apart from the holder are main violations of the so-called baseline necessities that main browser makers impose on CAs as a situation of being trusted by their software program.
Symantec’s transgressions have been critical. But given Symantec’s standing on the time as one of many greatest issuers of certificates, Google and different stakeholders have been in a bind. If Google or different browser makers have been to nullify all the Symantec-issued certificates in a single day, it would trigger widespread outages. The chaos that will consequence made the issuer too huge to fail. The penalties outlined by Google aimed to reduce such disruptions whereas exacting a significant punishment.
Over the following two years, browser makers and different corporations that depend on digital certificates to safe Internet communications step by step phased out belief within the certificates. Most timetables known as for a deadline someday in 2019. For causes Microsoft has but to elucidate, Windows continued to belief the basis certificates to signal software program.
That belief was lastly revoked—or at the very least suspended—on Tuesday, as soon as once more with no rationalization or discover. The transfer despatched sys admins scrambling to find out why customers have been receiving certificate errors when attempting to run software program corresponding to QuickBooks and AvaTax. Eventually, the CEO of safety agency Airlock Digital traced the trigger to the unannounced change in Windows.
A Microsoft consultant provided to offer remark for this story on the situation the knowledge not be attributed to Microsoft in any approach. Ars declined.
It’s doubtless that Microsoft delayed the revocation of the certificate for app-signing functions as a result of certificates in apps can’t be up to date as simply as they’ll for web sites. With no steering from the corporate, folks troubleshooting error messages are on their very own.
One possibility for resolving issues is to replace affected apps. By now, most apps have doubtless been up to date to make use of certificates not associated to those which have been blocked. By default, Windows has a function generally known as automated root updates turned on. Some customers have it turned off for varied causes, a lot of them professional. The above-linked Reddit thread additionally supplies a number of scripts folks can run to rotate out the basis certificate.
Update: 10 minutes after Ars declined Microsoft’s provide for a not-for-attribution remark, an organization consultant despatched the next assertion:
The VeriSign Class 3 Public Primary Certification Authority – G5 is distrusted as of 2019 and was set to “NotBefore” in a earlier launch. This signifies that certificates issued after the NotBefore date will now not be trusted; nonetheless, certificates issued earlier than the NotBefore date will proceed to be trusted. In our August Certificate Trust List replace, we modified this setting to Disable as part of our common deprecation course of which prompted some prospects with particular configurations to run into points. On August 24, 2023, we rolled again this transformation to assist remediate these points.

