Large language models (LLMs), corresponding to GPT-3 and PaLM, have proven spectacular progress lately, which have been pushed by scaling up models and coaching information sizes. Nonetheless, an extended standing debate has been whether or not LLMs can reason symbolically (i.e., manipulating symbols based mostly on logical guidelines). For instance, LLMs are ready to carry out easy arithmetic operations when numbers are small, however wrestle to carry out with massive numbers. This means that LLMs haven’t discovered the underlying guidelines wanted to carry out these arithmetic operations.
While neural networks have highly effective sample matching capabilities, they’re inclined to overfitting to spurious statistical patterns within the information. This doesn’t hinder good efficiency when the coaching information is massive and various and the analysis is in-distribution. However, for duties that require rule-based reasoning (corresponding to addition), LLMs wrestle with out-of-distribution generalization as spurious correlations within the coaching information are sometimes a lot simpler to exploit than the true rule-based answer. As a end result, regardless of vital progress in a wide range of pure language processing duties, efficiency on easy arithmetic duties like addition has remained a problem. Even with modest enchancment of GPT-4 on the MATH dataset, errors are nonetheless largely due to arithmetic and calculation errors. Thus, an necessary query is whether or not LLMs are able to algorithmic reasoning, which entails fixing a activity by making use of a set of summary guidelines that outline the algorithm.
In “Teaching Algorithmic Reasoning via In-Context Learning”, we describe an strategy that leverages in-context studying to allow algorithmic reasoning capabilities in LLMs. In-context studying refers to a mannequin’s potential to carry out a activity after seeing a number of examples of it throughout the context of the mannequin. The activity is specified to the mannequin utilizing a immediate, with out the necessity for weight updates. We additionally current a novel algorithmic prompting approach that permits normal goal language models to obtain robust generalization on arithmetic issues which can be tougher than these seen within the immediate. Finally, we display {that a} mannequin can reliably execute algorithms on out-of-distribution examples with an acceptable alternative of prompting technique.
 |
| By offering algorithmic prompts, we will train a mannequin the foundations of arithmetic through in-context studying. In this instance, the LLM (phrase predictor) outputs the proper reply when prompted with a straightforward addition query (e.g., 267+197), however fails when requested an identical addition query with longer digits. However, when the tougher query is appended with an algorithmic immediate for addition (blue field with white + proven beneath the phrase predictor), the mannequin is in a position to reply accurately. Moreover, the mannequin is able to simulating the multiplication algorithm (X) by composing a sequence of addition calculations. |
Teaching an algorithm as a ability
In order to train a mannequin an algorithm as a ability, we develop algorithmic prompting, which builds upon different rationale-augmented approaches (e.g., scratchpad and chain-of-thought). Algorithmic prompting extracts algorithmic reasoning talents from LLMs, and has two notable distinctions in contrast to different prompting approaches: (1) it solves duties by outputting the steps wanted for an algorithmic answer, and (2) it explains every algorithmic step with enough element so there isn’t any room for misinterpretation by the LLM.
To achieve instinct for algorithmic prompting, let’s think about the duty of two-number addition. In a scratchpad-style immediate, we course of every digit from proper to left and hold monitor of the carry worth (i.e., we add a 1 to the following digit if the present digit is larger than 9) at every step. However, the rule of carry is ambiguous after seeing just a few examples of carry values. We discover that together with express equations to describe the rule of carry helps the mannequin give attention to the related particulars and interpret the immediate extra precisely. We use this perception to develop an algorithmic immediate for two-number addition, the place we offer express equations for every step of computation and describe varied indexing operations in non-ambiguous codecs.
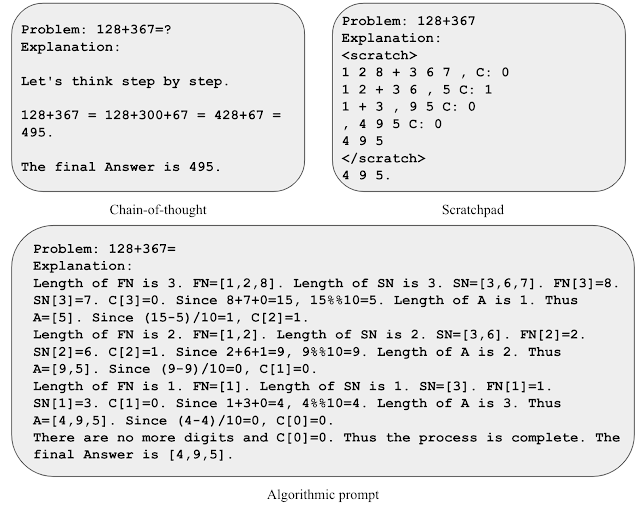 |
| Illustration of assorted immediate methods for addition. |
Using solely three immediate examples of addition with reply size up to 5 digits, we consider efficiency on additions of up to 19 digits. Accuracy is measured over 2,000 complete examples sampled uniformly over the size of the reply. As proven beneath, using algorithmic prompts maintains excessive accuracy for questions considerably longer than what’s seen within the immediate, which demonstrates that the mannequin is certainly fixing the duty by executing an input-agnostic algorithm.
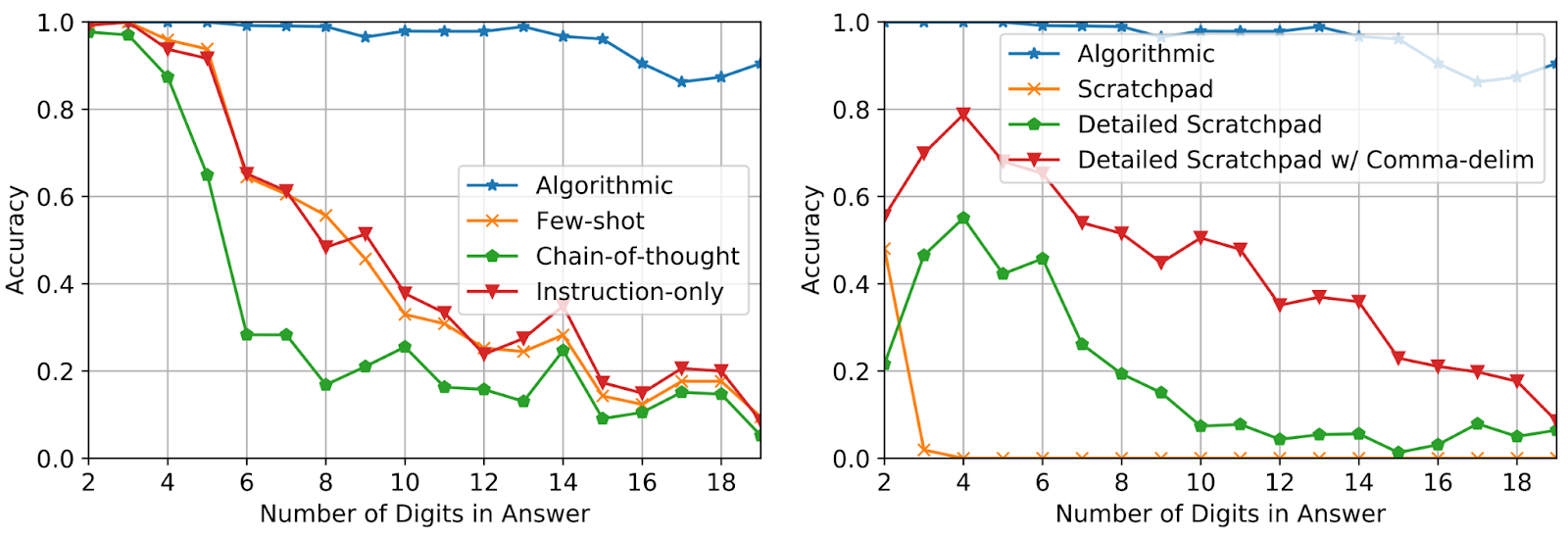 |
| Test accuracy on addition questions of accelerating size for various prompting strategies. |
Leveraging algorithmic abilities as software use
To consider if the mannequin can leverage algorithmic reasoning in a broader reasoning course of, we consider efficiency utilizing grade college math phrase issues (GSM8k). We particularly try to substitute addition calculations from GSM8k with an algorithmic answer.
Motivated by context size limitations and attainable interference between totally different algorithms, we discover a technique the place differently-prompted models work together with each other to clear up complicated duties. In the context of GSM8k, now we have one mannequin that makes a speciality of casual mathematical reasoning utilizing chain-of-thought prompting, and a second mannequin that makes a speciality of addition utilizing algorithmic prompting. The casual mathematical reasoning mannequin is prompted to output specialised tokens so as to name on the addition-prompted mannequin to carry out the arithmetic steps. We extract the queries between tokens, ship them to the addition-model and return the reply to the primary mannequin, after which the primary mannequin continues its output. We consider our strategy utilizing a troublesome downside from the GSM8k (GSM8k-Hard), the place we randomly choose 50 addition-only questions and improve the numerical values within the questions.
 |
| An instance from the GSM8k-Hard dataset. The chain-of-thought immediate is augmented with brackets to point out when an algorithmic name must be carried out. |
We discover that utilizing separate contexts and models with specialised prompts is an efficient approach to sort out GSM8k-Hard. Below, we observe that the efficiency of the mannequin with algorithmic name for addition is 2.3x the chain-of-thought baseline. Finally, this technique presents an instance of fixing complicated duties by facilitating interactions between LLMs specialised to totally different abilities through in-context studying.
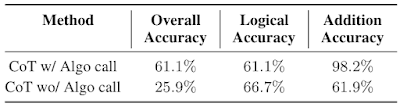 |
| Chain-of-thought (CoT) efficiency on GSM8k-Hard with or with out algorithmic name. |
Conclusion
We current an strategy that leverages in-context studying and a novel algorithmic prompting approach to unlock algorithmic reasoning talents in LLMs. Our outcomes recommend that it might be attainable to remodel longer context into higher reasoning efficiency by offering extra detailed explanations. Thus, these findings level to the power of utilizing or in any other case simulating lengthy contexts and producing extra informative rationales as promising analysis instructions.
Acknowledgements
We thank our co-authors Behnam Neyshabur, Azade Nova, Hugo Larochelle and Aaron Courville for his or her helpful contributions to the paper and nice suggestions on the weblog. We thank Tom Small for creating the animations on this publish. This work was accomplished throughout Hattie Zhou’s internship at Google Research.

