If you have been informed that the largest residing factor in the world and the largest synthetic construction ever created belonged to the subterranean realm, you’ll in all probability discover it laborious to imagine. Well, the first case is the mycelium of a fungus in Oregon (USA), which covers eight hundred and ninety hectares; and the second is a metropolis of termite mounds with an space of 100 and forty thousand sq. miles in Brazil. It is yet one more instance of the nice secrets and techniques that the subsoil and its fauna harbor. A greater understanding of what goes on down there’s essential for the improvement of agriculture or building. Now a brand new technological breakthrough guarantees to make this analysis simpler. It is a burrowing robotic impressed by a Pacific crab.
EMBUR: the robotic crab that may analysis the subsoil
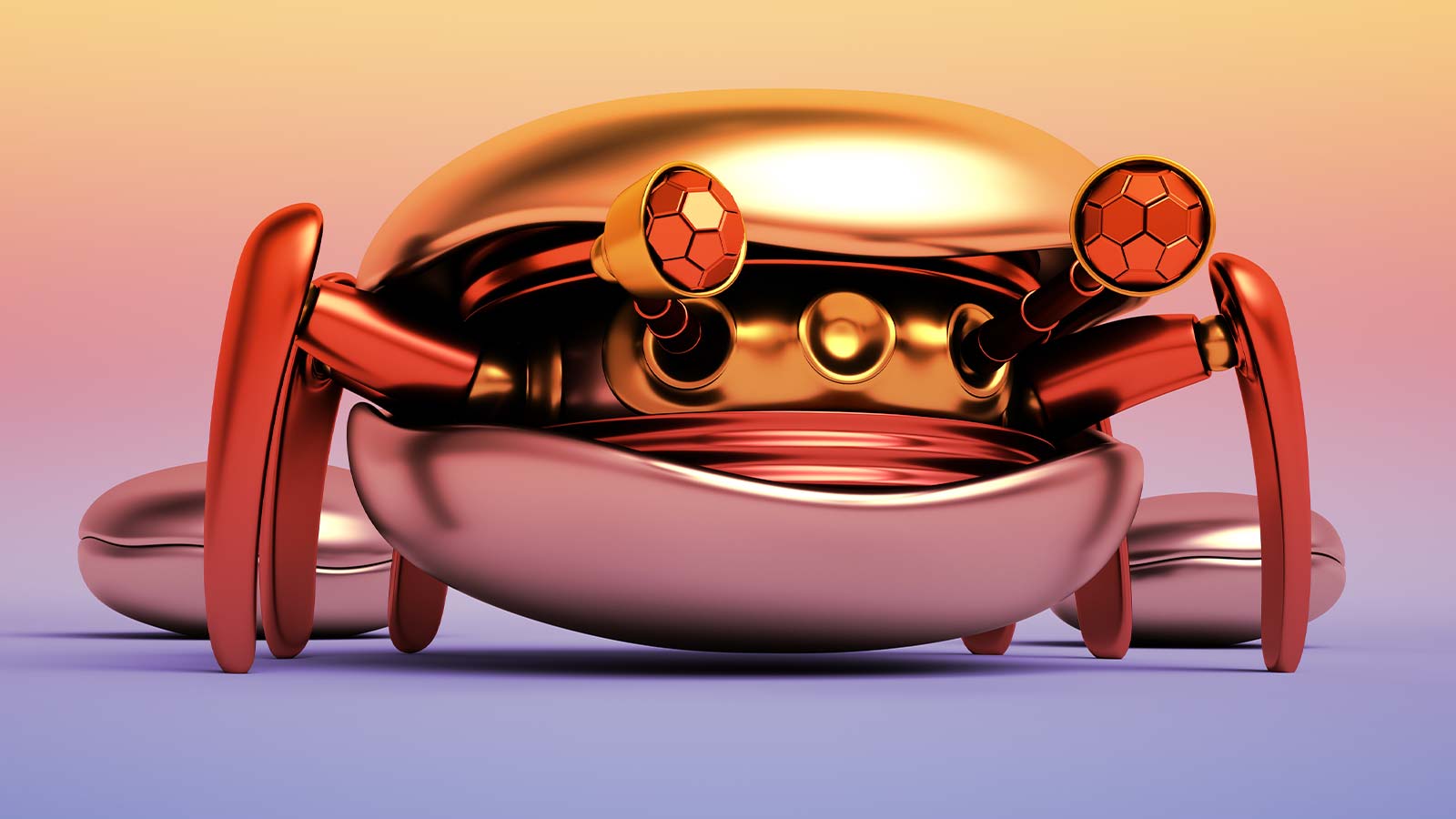
The mole or sand crab – scientifically generally known as Emerita analoga – is a crustacean that has opted for a survival technique in opposition to predatory birds. Its habitat is the sand close to the shore the place, when the waves retreat, it buries itself rapidly by burrowing with its legs. From there it makes use of its antennae to breathe and feed on phytoplankton.
The mole or sand crab – scientifically generally known as Emerita analoga – is a crustacean that has opted for a survival technique in opposition to predatory birds. Its habitat is the sand close to the shore the place, when the waves retreat, it buries itself rapidly by burrowing with its legs. From there, it makes use of its antennae to breathe and feed on phytoplankton.
Well, in a brand new instance of biomimicry, it’s this function that has impressed a gaggle of scientists at the University of Berkley to develop the EMBER (an acronym for EMerita BUrrowing Robot.)
The foremost function of the new robotic system is that it might probably burrow into the floor and enter it vertically, simply as the mole crab does. This sort of system faces two elementary challenges. On the one hand, there’s the undeniable fact that the deeper the depth, the extra resistance the floor provides. On the different hand, throughout this course of, grains of sand and mud particles find yourself accumulating of their synthetic joints. Scientists at the University of Berkley have give you two options.
First, patterned after the mole crab, they designed a robotic with legs that provide an anisotropic drive response. They apply rather more drive in a single course than in one other. Just assume of a swimmer that applies its drive by extending its limbs. Thus, the researchers copied the insertion, sweeping, and retraction of the crab’s legs after which used Resistive Force Theory (RFT) to mannequin the utilized drive.
Secondly, they’ve resorted to a cuticle impressed by the mole crab, this time in its arthrodial membrane. This is a delicate materials that covers the uncovered elements of the joints and prevents the entry of overseas our bodies.
Now, the improvement workforce is engaged on replicating the mole crab’s different capabilities in order that the EMBUR can swim, burrow and transfer via the sand on the seaside.
According to EMBUR’s builders, robotics has made nice advances in the aerial, aquatic and terrestrial environments with machines comparable to drones and underwater robots. Subway exploration, on the different hand, remained a pending topic, aside from autonomous machines utilized in mining.
This new robotic or its extra superior variations shall be half of a era of methods designed to investigate the subsoil in areas comparable to agriculture, marine conservation, and even building.
A robotic canine patrolling the bowels of the earth
If you comply with our web site, you should have seen multiple article on building applied sciences: from exoskeletons to hold heavy weights to wearables to forestall work-related accidents. Drones are additionally one other instruments beginning for use in these environments. However, one of the most hanging functions we now have seen lately is the use of SPOT, the Boston Dynamics robotic canine.
ACCIONA’s infrastructure division makes use of it in some of its initiatives for various functions, some associated to the subsoil. Thanks to the sensors it incorporates, SPOT captures thermal pictures of the setting, scans tunnels, and offers geological reviews complementing the work of the large tunnel-boring machines that, in a method, are the huge brothers of the EMBUR. You can see SPOT in motion on this video:
@acciona_official ¿Pueden ir juntas #tecnología y #seguridad? En ACCIONA sí 🐕🤖 #innovación #construcción #parati #perro #robotic ♬ unique sound – Encanto fp;)
Source:

