8:45 pm EDT replace: The launch of an Atlas V rocket with the Silent Barker mission has been postponed from Tuesday as a consequence of Tropical Storm Idalia. “Out of an abundance of warning for personnel security, a essential nationwide safety payload and the approaching Tropical Storm Idalia, the crew made the choice to return the rocket and payload to the vertical integration facility (VIF),” ULA mentioned. “We will work with our prospects and the vary to substantiate our subsequent launch try and a new date will likely be supplied as soon as it’s secure to launch.”
Original submit: The National Reconnaissance Office does not sometimes discuss about any of its missions, however in an uncommon break with precedent, the button-down spy satellite agency is taking a unique tack with its subsequent launch Tuesday from Cape Canaveral, Florida.
“We’re attempting to be extra clear and share extra info,” mentioned Chris Scolese, director of the National Reconnaissance Office, in a roundtable with reporters Monday. As extra international locations and firms launch missions into house, Scolese mentioned the house atmosphere is turning into extra congested, contested, and aggressive.
“It’s additionally turning into simpler and simpler to see what’s going up there,” Scolese mentioned. “We wish to let individuals know, to some extent, what our capabilities are.”
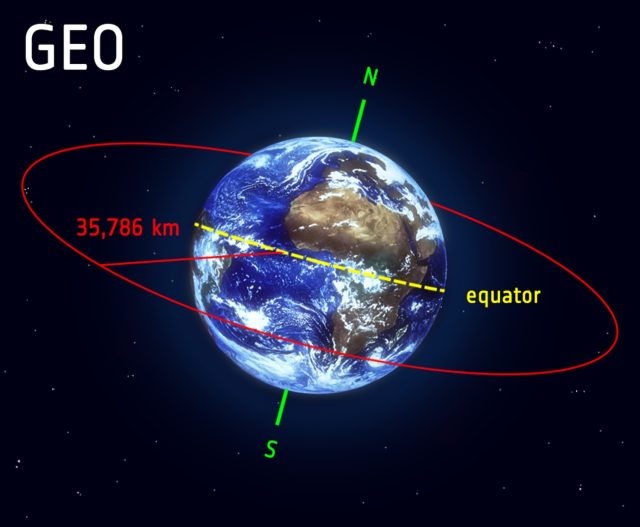
The NRO has a number of satellites—officers will not say precisely what number of—mounted on prime of a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket for liftoff at 8:34 am EDT (12:34 UTC) from Cape Canaveral Space Force Station. Their vacation spot is geosynchronous orbit, a belt of satellites positioned greater than 22,000 miles (almost 36,000 kilometers) over the equator.
In geosynchronous orbit, a spacecraft completes one lap round Earth on the similar price because the planet’s rotation, giving a satellite a continuing view of the identical geographic area. That makes geosynchronous orbit a preferred location for communications satellites, climate observatories, and platforms to detect the primary signal of a missile assault.
The US Space Force and the NRO have quite a few satellites in geosynchronous orbit, and the mission poised for liftoff Tuesday will assist observe potential threats to these multibillion-dollar belongings.
“Geosynchronous orbit is far away,” Scolese said. “Ground-based systems have a harder time seeing what’s up there. This provides us the capability of being in this same orbit, so that we’re closer to what’s happening up there. It will not be looking at the ground, it will be looking at space.”
You can watch Tuesday’s launch on ULA’s reside webcast, which we’ve embedded on this web page.
Bark or chew?
This new mission additionally has a handy guide a rough code title—Silent Barker—and an attention-grabbing mission patch, which is not uncommon for launches with NRO spy satellites.
The NRO and the Space Force are companions on the Silent Barker mission. The NRO managed the event of the satellites and can function them as soon as they’re in orbit, whereas the Space Force is offering the launch on ULA’s Atlas V rocket.
The Silent Barker satellites will detect and regularly observe different objects in geostationary orbit, a functionality that navy leaders have prioritized over the past decade. In that point, Pentagon officers say there was an escalation in “cat and mouse” video games between US satellites and people operated by China and Russia.
US officers have highlighted a number of occurrences of Russian inspector satellites approaching US spy satellites flying in low-Earth orbit lately. Higher up in geosynchronous orbit, one other mysterious Russian navy satellite has roamed close to quite a few industrial communications satellites and a French-Italian navy spacecraft, elevating issues that it might be attempting to intercept radio alerts.
The US navy already has its personal satellites able to approaching different objects in geosynchronous orbit. These satellites, a part of the Space Force’s Geosynchronous Space Situational Awareness Program (GSSAP) program, had been a part of an orbital dance with two Chinese navy satellites final 12 months.
The US navy dispatched one of many GSSAP satellites to get a better have a look at the 2 Chinese spacecraft, however the Chinese satellites took off in reverse instructions. Then one of many Chinese spacecraft settled right into a place to get a sunlit view of the Space Force surveillance satellite that had been chasing it.
So far, there have not been studies that any of those cat-and-mouse video games have resulted in a bodily or cyberattack on a US navy satellite, however that is what the Silent Barker mission is designed to protect towards.

“The thought of the mission is to place a satellite into geosynchronous orbit after which to be that orbital regime and get a way of what’s occurring each day,” Scolese mentioned. “Satellites do transfer in geosynchronous orbit. You’ve heard about communications satellites transferring from one location to a different to supply higher protection to different areas.”
Officials haven’t disclosed what corporations had been concerned in constructing the Silent Barker satellites or what sort of sensors the spacecraft will use. The price range for this system additionally stays a secret.
“Certainly, we wish to have the ability to see that so we all know what’s happening within the space, however we additionally wish to know if one thing is occurring that’s surprising, or shouldn’t be happening, that would doubtlessly characterize a risk to a high-value asset, both our’s or one among our allies,” Scolese mentioned.
He known as the Silent Barker mission a “watchdog” in geosynchronous orbit. That’s comparable nomenclature to the “neighborhood watch” description the Space Force has used for the GSSAP satellites. A key distinction between the Silent Barker and GSSAP packages, in response to navy officers, is the power of the Silent Barker satellites to repeatedly monitor the place, or “preserve custody,” of different objects in geosynchronous orbit.
“What Silent Barker goes to do is present that indication and warning (of a potential risk to a US satellite), so it might inform selections about what we do or don’t have to do by way of maneuvers or consciousness,” Scolese mentioned.
“The functionality that we’re going launch tomorrow goes an extended approach to giving us aggressive endurance and aggressive benefit in house to verify we not solely see, however preserve custody of the threats in GEO (geosynchronous orbit),” mentioned Lt. Gen. Michael Guetlein, who heads US Space Systems Command, which oversees the navy’s procurement of satellites and rockets.
The navy at the moment depends totally on ground-based radars to scan geosynchronous orbit. Silent Barker follows up on a devoted navy surveillance satellite that launched in 2010 with an optical sensor to lookup at geosynchronous orbit from low-Earth orbit, just some hundred miles above Earth.
Placing the Silent Barker sensors nearer to their observational targets will give the NRO and the Space Force a new set of eyes in geosynchronous orbit. Ground radars include limitations as a result of they’ll solely see a part of the sky at a given time, and there are components just like the climate to think about. The radars can also solely detect an object about the dimensions of a basketball or bigger. Silent Barker will see smaller objects and will not be topic to terrestrial limitations.

