Arian Zwegers/CC BY 2.0
For centuries, Western students have touted the destiny of the native inhabitants on Easter Island (Rapa Nui) as a case examine in the devastating value of environmentally unsustainable dwelling. The story goes that the folks on the distant island chopped down all the timber to construct large stone statues, triggering a inhabitants collapse. Their numbers have been additional depleted when Europeans found the island and introduced international illnesses, amongst different components. But an alternate narrative started to emerge in the twenty first century that the earliest inhabitants truly lived fairly sustainably till that time. A brand new paper revealed in the journal Science Advances gives one other key piece of evidence in assist of that different speculation.
As beforehand reported, Easter Island is known for its large monumental statues, referred to as moai, constructed some 800 years in the past and sometimes mounted on platforms referred to as ahu. Scholars have puzzled over the moai on Easter Island for many years, pondering their cultural significance, in addition to how a Stone Age tradition managed to carve and transport statues weighing as a lot as 92 tons. The first Europeans arrived in the seventeenth century and located just a few thousand inhabitants on a tiny island (simply 14 by 7 miles throughout) 1000’s of miles away from every other land. Since then, in an effort to clarify the presence of so many moai, the assumption has been that the island was as soon as dwelling to tens of 1000’s of folks.
But maybe they did not want tens of 1000’s of folks to perform that feat. Back in 2012, Carl Lipo of Binghamton University and Terry Hunt of the University of Arizona confirmed that you might transport a 10-foot, 5-ton moai a number of hundred yards with simply 18 folks and three sturdy ropes by using a rocking movement. In 2018, Lipo proposed an intriguing speculation for a way the islanders positioned pink hats on high of some moai; these can weigh as much as 13 tons. He instructed the inhabitants used ropes to roll the hats up a ramp. Lipo and his group later concluded (based mostly on quantitative spatial modeling) that the islanders probably selected the statues’ areas based mostly on the availability of recent water sources, per a 2019 paper in PLOS One.
In 2020, Lipo and his group turned their consideration to establishing a greater chronology of human occupation of Rapa Nui. While it is typically agreed that individuals arrived in Eastern Polynesia and on Rapa Nui someday in the late twelfth century or early thirteenth century, we do not actually know very a lot about the timing and tempo of occasions associated to ahu development and moai transport specifically.
In his bestselling 2005 ebook Collapse, Jared Diamond supplied the societal collapse of Easter Island (aka Rapa Nui), round 1600, as a cautionary story. Diamond controversially argued that the destruction of the island’s ecological atmosphere triggered a downward spiral of inside warfare, inhabitants decline, and cannibalism, leading to an eventual breakdown of social and political constructions.
Challenging a story
Lipo has lengthy challenged that narrative, arguing way back to 2007 against the “ecocide” theory. He and Hunt revealed a paper that yr noting the lack of evidence of any warfare on Easter Island in comparison with different Polynesian islands. There are not any recognized fortifications, and the obsidian instruments discovered have been clearly used for agriculture. Nor is there a lot evidence of violence amongst skeletal stays. He and Hunt concluded that the folks of Rapa Nui continued to thrive properly after 1600, which might warrant a rethinking of the in style narrative that the island was destitute when Europeans arrived in 1722.
For their 2020 examine, the group utilized a Bayesian model-based technique to current radiocarbon dates collected from prior excavations at 11 totally different websites with ahu. That work met with some combined opinions from Lipo’s fellow archaeologists, with some suggesting that his group cherry-picked its radiocarbon courting—an allegation he dismissed at the time as “merely baloney and misinformed considering.” They filtered their radiocarbon samples to only these they have been assured associated to human occupation and human-related occasions, that means they analyzed a smaller subset of all the obtainable ages—not an uncommon technique to remove bias as a result of points with previous carbon—and the outcomes for colonization estimates have been about the similar as earlier than.

Robert J. DiNapoli
The mannequin additionally built-in the order and place of the island’s distinctive structure, in addition to ethnohistoric accounts, thereby quantifying the onset of monument development, the charge at which it occurred, and when it probably ended. This allowed the researchers to check Diamond’s “collapse” speculation by constructing a more exact timeline of when development passed off at every of the websites. The outcomes demonstrated an absence of evidence for a pre-contact collapse and as an alternative supplied sturdy assist for a brand new rising mannequin of resilient communities that continued their long-term traditions regardless of the impacts of European arrival.
Fresh evidence
Now Lipo is again with recent findings in assist of his different theory, having analyzed the panorama to determine all the agricultural areas on the island. “We actually needed to have a look at the evidence for whether or not the island may in actual fact assist such a big quantity of folks,” he stated throughout a media briefing. “What we find out about the pre-contact folks dwelling on the island is that they survived on a mixture of marine sources—fishing accounted for about 50 p.c of their weight loss program—and rising crops,” significantly the candy potato, in addition to taro and yams.
He and his co-authors got down to decide how a lot meals might be produced agriculturally, extrapolating from that the dimension of a sustainable inhabitants. The volcanic soil on Easter Island is very weathered and thus poor in vitamins important for plant progress: nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium primarily, but in addition calcium, magnesium, and sulfur. To enhance yields, the natives initially minimize down the island’s timber to get vitamins again into the soil.
When there have been no more timber, they engaged in a observe referred to as “lithic mulching,” a kind of rock gardening through which damaged rocks have been added to the first 20 to 25 centimeters (about 8 to 10 inches) of soil. This added important vitamins again into the soil. “We do it ourselves with non-organic fertilizer,” stated Lipo. “Essentially we use machines to crush rock into tiny items, which is efficient as a result of it exposes rather a lot of floor space. The folks in Rapa Nui are doing it by hand, actually breaking apart rocks and sticking them in dust.”
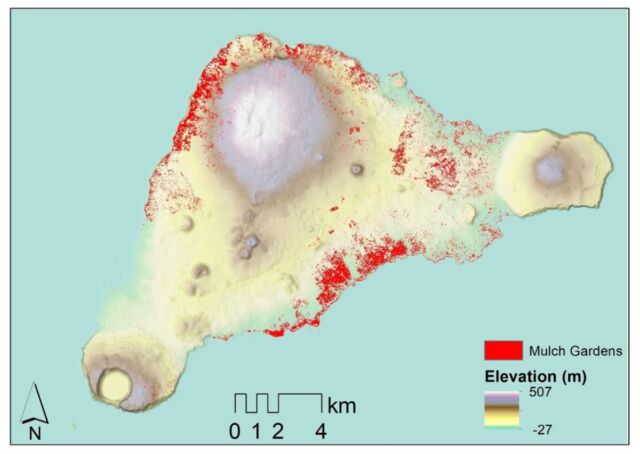
There had been just one 2013 examine geared toward figuring out the island’s rock-garden capability, which relied on near-infrared bands from satellite tv for pc photos. The authors of that examine estimated that between 4.9 and 21.2 km2 of the island’s whole space comprised rock gardens, though they acknowledged this was probably an inaccurate estimation.
Carl Lipo
Lipo et al. examined satellite tv for pc imagery knowledge collected over the final 5 years, not simply in the near-infrared, but in addition short-wave infrared (SWIR) and different seen spectra. SWIR is especially delicate to detecting water and nitrogen ranges, making it simpler to pinpoint areas the place lithic mulching occurred. They skilled machine-learning fashions on archaeological area identifications of rock backyard options to research the SWIR knowledge for a brand new estimation of capability.
The end result: Lipo et al. decided that the prevalence of rock gardening was about one-fifth of even the most conservative earlier estimates of inhabitants dimension on Easter Island. They estimate that the island may assist about 3,000 folks—roughly the similar quantity of inhabitants European explorers encountered once they arrived. “Previous research had estimated that the island was pretty lined with mulch gardening, which led to estimates of as much as 16,000 folks,” stated Lipo. “We’re saying that the island may by no means have supported 16,000 folks; it did not have the productiveness to take action. This pre-European collapse narrative merely has no foundation in the archaeological document.”
“We do not see demographic change decline in populations previous to Europeans’ arrival,” Lipo stated. “All the [cumulative] evidence so far reveals a steady progress till some plateau is reached. It actually was by no means a simple place to dwell, however folks have been in a position to determine a method of doing so and lived inside the boundaries of the capability of the island up till European arrival.” So quite than being a cautionary story, “Easter Island is a good case of how populations adapt to restricted sources on a finite place, and accomplish that sustainably.”
DOI: Science Advances, 2024. 10.1126/sciadv.ado1459 (About DOIs).
Binghamton University archaeologist Carl Lipo has make clear some of the historic mysteries of Easter Island (Rapa Nui) by his ongoing analysis. Credit: Binghamton University, State University of New York

