Excerpted from WHY WE DIE: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for Immortality by Venki Ramakrishnan with permission from William Morrow, an imprint of HarperCollins. Copyright © 2024 by Venki Ramakrishnan.
Lessons from a Lowly Worm
We all know households of long-lived people. But precisely how a lot do genes affect longevity? A research of two,700 Danish twins advised that the heritability of human longevity—a quantitative measure of how a lot variations in genes account for variations of their ages at demise—was solely about 25 %. Further, these genetic components have been regarded as as a result of sum of small results from a massive variety of genes, and due to this fact troublesome to pinpoint on the extent of a person gene. By the time that the Danish research was carried out in 1996, a lowly worm was already serving to to overturn that concept.
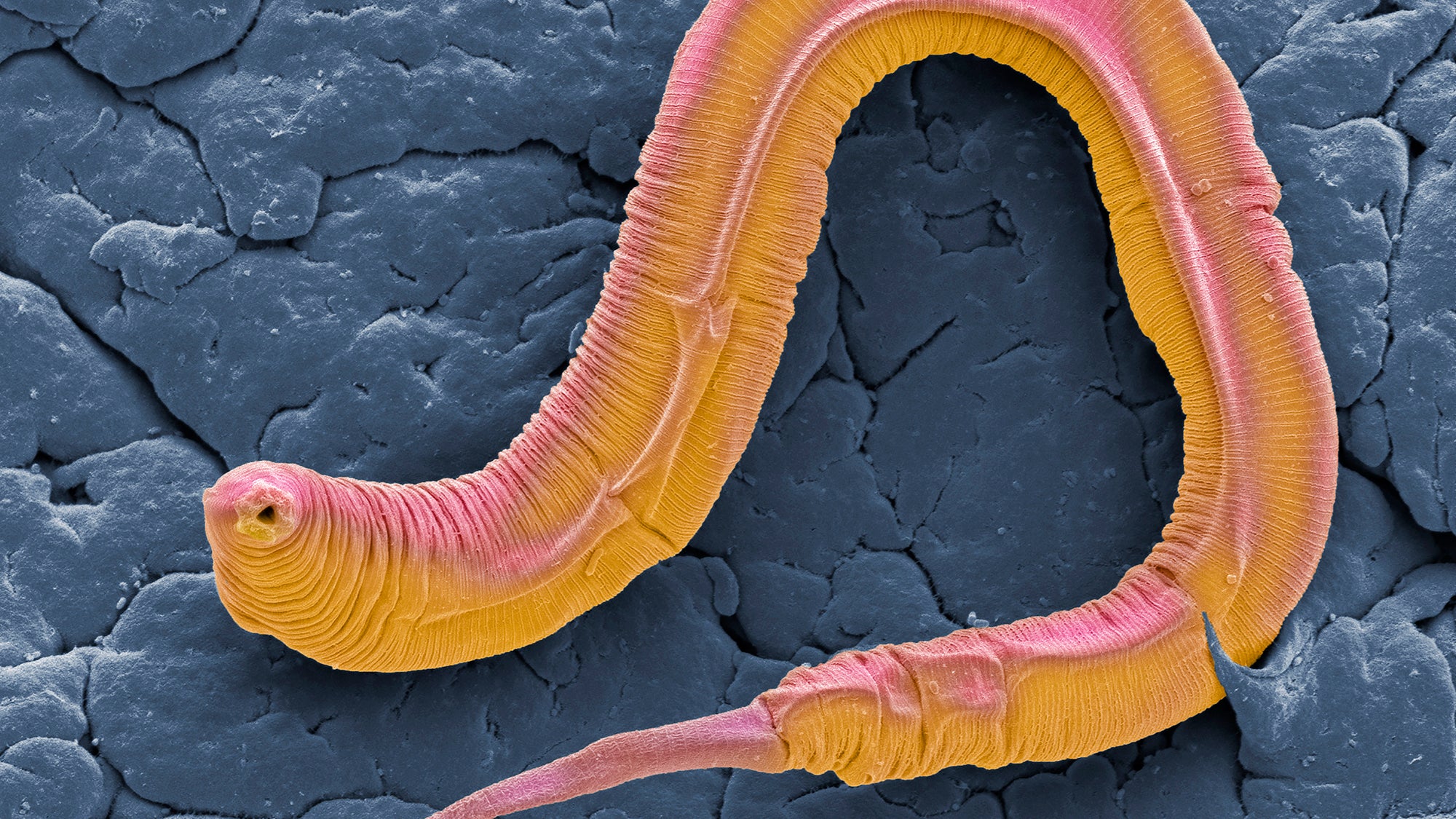
That lowly worm was the soil nematode Caenorhabditis elegans, launched into fashionable biology by Sydney Brenner, a large of the sphere recognized for his caustic wit. Born and initially educated in South Africa, he spent a lot of his productive life in Cambridge, England, earlier than he established labs everywhere in the world from California to Singapore, main a few of us to comment that the solar by no means set on the Brenner Empire. He first turned well-known for having found mRNA. More usually, he labored intently with Francis Crick on the character of the genetic code and the way it was learn to make proteins. Once he and Crick determined that they’d solved the basic drawback of utilizing genetic info to make proteins, Brenner turned his consideration to investigating how a complicated animal develops from a single cell, and the way the mind and its nervous system work.
Brenner recognized C. elegans as a perfect organism to review as a result of it could possibly be grown simply, had a comparatively brief technology time, and was clear, so you may see the cells that made up the worm. He skilled a variety of scientists on the MRC Laboratory of Molecular Biology in Cambridge and spawned a complete worldwide group of researchers finding out C. elegans for all the pieces from growth to conduct. Among his colleagues was biologist John Sulston, whom you met in chapter 5. One of Sulston’s extra outstanding tasks was to painstakingly hint the lineage of every of the roughly 9 hundred cells within the mature worm all the way in which from the one unique cell, which led to an surprising discovery: sure cells are programmed to die at exact phases of growth. Scientists went on to determine the genes that despatched these cells to commit suicide at simply the fitting time to ensure that the organism to develop.
For an animal with solely 9 hundred cells, these worms are extremely complicated. They have a few of the identical organs as bigger animals however in easier kind: a mouth, an gut, muscle tissues, and a mind and nervous system. They don’t have a circulatory or respiratory system. Though tiny—solely about a millimeter lengthy—nematodes can simply be seen wriggling round underneath a microscope. Being hermaphrodites, they produce each sperm and egg, however C. elegans may reproduce asexually underneath some circumstances. They are usually social, however scientists have discovered mutations that make them delinquent. Worms feed on micro organism, and similar to micro organism, they’re cultivated in petri dishes within the lab. They may be frozen away indefinitely in small vials in liquid nitrogen and easily thawed and revived when wanted.
Worms sometimes stay for a couple of weeks. However, when confronted with hunger, they will go into a dormant state referred to as dauer (associated to the German phrase for endurance), through which they will survive for as much as two months earlier than reemerging when vitamins are plentiful once more. Relative to people’ life span, this is able to be the equal of 300 years. Somehow these worms have managed to droop the traditional means of growing older. There is a caveat, although: solely juvenile worms can enter the dauer state. Once animals undergo puberty and develop into adults, they now not have this feature.
David Hirsh turned keen on C. elegans whereas he was a analysis fellow underneath Brenner at Cambridge, then continued working with the worms upon becoming a member of the college on the University of Colorado. There he took on a postdoc named Michael Klass, who needed to focus on growing older.
This was at a time when growing older was merely regarded as a regular and inevitable course of of damage and tear, and mainstream biologists seen growing older analysis with some disdain. However, issues have been starting to vary, partly as a result of the US authorities was involved about an growing older inhabitants. As Hirsh recalled, the National Institutes of Health had simply established the National Institute on Aging, and a minimum of a few of his and Klass’s motivation for working within the space was that they knew they stood a good probability of receiving federal funding.
Hirsh and Klass first confirmed that, by many standards, worms age little if in any respect within the dauer state. Next, Klass needed to see if he might isolate mutants of worms that may stay longer however not essentially go into dormancy. This would assist him determine genes that affected life span. To quickly produce mutants that he might display screen for longevity, he handled the nematodes with mutagenic chemical substances. He ended up with 1000’s of plates of worms, which he continued finding out after beginning his personal lab in Texas. In 1983 Klass revealed a paper with a few long- lived mutant nematodes, however ultimately he shut down his lab and joined Abbott Laboratories close to Chicago. Before doing so, nevertheless, he despatched a frozen batch of his mutant worms to a former colleague from Colorado, Tom Johnson, who by then was on the University of California, Irvine.
By inbreeding a few of the mutant worms, Johnson discovered that their imply life span assorted from ten to thirty-one days, from which he deduced that, a minimum of in worms, life span concerned a substantial genetic element. It nonetheless wasn’t clear what number of genes affected life span, however in 1988 Johnson, working with an enthusiastic undergraduate scholar named David Friedman, got here to a hanging conclusion that ran fully counter to the standard knowledge that many genes, every making small contributions, influenced longevity. Instead, it turned out that a mutation in a single gene, which the 2 referred to as age-1, conferred a longer life span. Johnson went on to indicate that worms with the age-1 mutation had decrease mortality in any respect ages, whereas their most life span greater than doubled that of regular worms. Maximum life span, outlined because the life span of the highest 10 % of the inhabitants, is taken into account a higher measure of growing older results as a result of imply life span may be affected by all types of different components that don’t essentially should do with growing older, comparable to environmental hazards and resistance to ailments.