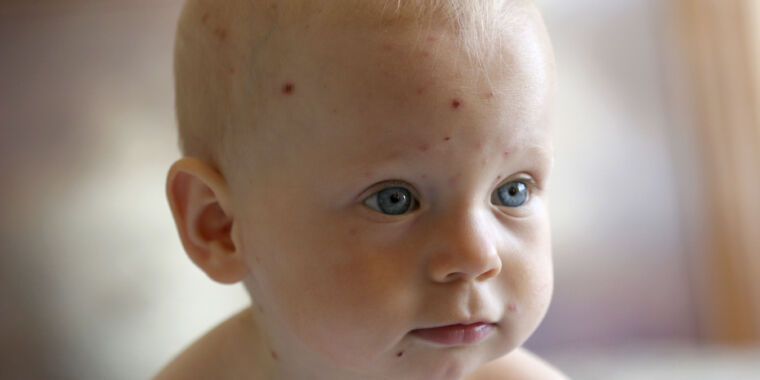
Thanks to the vaccination program that started in 1995, chickenpox is now comparatively uncommon. Cases of the depressing, itchy situation have fallen extra than 97 %. But, whereas youngsters have largely put the oatmeal baths and oven mitts behind them, docs have apparently let their diagnostic expertise get a bit crusty.
According to a study printed Thursday, public well being researchers in Minnesota discovered that 55 % of individuals identified with chickenpox primarily based on their signs had been really adverse for the varicella-zoster virus, the virus that causes chickenpox. The study famous that the individuals had been all identified in individual by well being care suppliers in medical services. But, as an alternative of chickenpox, lab testing confirmed that some of the sufferers had been really contaminated with an enterovirus, which may trigger a rash, or the herpes simplex virus 1, which causes chilly sores.
The study, printed within the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report, helps increasing laboratory testing for suspected chickenpox instances within the state’s program and highlights that diagnoses primarily based on signs are “unreliable.”
For one factor, docs merely see far fewer chickenpox instances today as a result of of the safety from vaccines. While chickenpox instances within the US beforehand reached 4 million every year, with 10,500 to 13,500 hospitalizations and 100 to 150 deaths, there are now fewer than 150,000 instances,1,400 hospitalizations, and 30 deaths every year, the CDC studies. Vaccination is extra than 90 % efficient at stopping the illness. In the uncommon instances the place a vaccinated individual contracts chickenpox, the muted rashes are difficult to establish by eye. But even in unvaccinated youngsters, chickenpox could be tough to select; it could actually simply be confused with measles, insect bites, enterovirus, pores and skin infections corresponding to scabies and impetigo, herpes viruses, and hand, foot, and mouth illness.
Since 2016, the Minnesota Department of Health has been working to broaden laboratory testing, together with outreach to well being care suppliers and the general public on the significance of testing to verify suspected chickenpox instances.
Between 2016 and 2023, 208 individuals who had been identified with chickenpox in individual at a medical facility submitted specimens for testing to the state well being division. Only 93 of the 208 (45 %) had been constructive for the virus. The vaccination standing was identified for 203 of the individuals—100 had been vaccinated, 103 weren’t. Of the vaccinated individuals examined, solely 22 (22 %) turned out to have chickenpox, whereas 68 (66 %) of the unvaccinated individuals had it, reflecting the efficacy of vaccination.
In a bigger group of 420 individuals, which included individuals who had been self-diagnosed, the accuracy fee was unsurprisingly decrease. Of the 420 suspected chickenpox instances, solely 157 (37 %) had been constructive for the varicella-zoster virus. Of the remaining 263 individuals, 47 had been constructive for enterovirus, 20 had been constructive for herpes simplex virus 1, 0 had been constructive for herpes simplex virus 2 (genital herpes), two individuals had indeterminate take a look at outcomes, and 194 had been adverse for all 4 viruses examined.
The authors spotlight that the findings are important as a result of individuals suspected of having chickenpox are beneficial to remain house from faculty and work longer than individuals with different viral infections. More testing can guarantee applicable medical administration.